SGN-B6A: A New Vedotin Antibody-Drug Conjugate Directed to Integrin Beta-6 for Multiple Carcinoma Indications
- PMID: 37619980
- PMCID: PMC10690100
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-22-0817
SGN-B6A: A New Vedotin Antibody-Drug Conjugate Directed to Integrin Beta-6 for Multiple Carcinoma Indications
Abstract
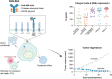
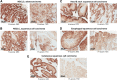
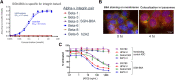
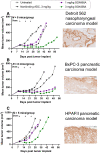
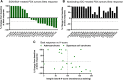
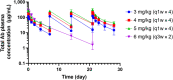
Integrin beta-6, a component of the heterodimeric adhesion receptor alpha-v/beta-6, is overexpressed in numerous solid tumors. Its expression has been shown by multiple investigators to be a negative prognostic indicator in diverse cancers including colorectal, non-small cell lung, gastric, and cervical. We developed SGN-B6A as an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) directed to integrin beta-6 to deliver the clinically validated payload monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) to cancer cells. The antibody component of SGN-B6A is specific for integrin beta-6 and does not bind other alpha-v family members. In preclinical studies, this ADC has demonstrated activity in vivo in models derived from non-small cell lung, pancreatic, pharyngeal, and bladder carcinomas spanning a range of antigen expression levels. In nonclinical toxicology studies in cynomolgus monkeys, doses of up to 5 mg/kg weekly for four doses or 6 mg/kg every 3 weeks for two doses were tolerated. Hematologic toxicities typical of MMAE ADCs were dose limiting, and no significant target-mediated toxicity was observed. A phase I first-in-human study is in progress to evaluate the safety and antitumor activity of SGN-B6A in a variety of solid tumors known to express integrin beta-6 (NCT04389632).
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
References
-
- Nemeth JA, Nakada MT, Trikha M, Lang Z, Gordon MS, Jayson GC, et al. . Alpha-v integrins as therapeutic targets in oncology. Cancer Invest 2007;25:632–46. - PubMed
-
- Bengs S, Becker E, Busenhart P, Spalinger MR, Raselli T, Kasper S, et al. . β6-integrin serves as a novel serum tumor marker for colorectal carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2019;145:678–85. - PubMed
-
- Elayadi AN, Samli KN, Prudkin L, Liu YH, Bian A, Xie XJ, et al. . A peptide selected by biopanning identifies the integrin alphavbeta6 as a prognostic biomarker for non–small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 2007;67:5889–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

