Principles and methods for transferring polygenic risk scores across global populations
- PMID: 37620596
- PMCID: PMC10961971
- DOI: 10.1038/s41576-023-00637-2
Principles and methods for transferring polygenic risk scores across global populations
Abstract
Polygenic risk scores (PRSs) summarize the genetic predisposition of a complex human trait or disease and may become a valuable tool for advancing precision medicine. However, PRSs that are developed in populations of predominantly European genetic ancestries can increase health disparities due to poor predictive performance in individuals of diverse and complex genetic ancestries. We describe genetic and modifiable risk factors that limit the transferability of PRSs across populations and review the strengths and weaknesses of existing PRS construction methods for diverse ancestries. Developing PRSs that benefit global populations in research and clinical settings provides an opportunity for innovation and is essential for health equity.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Figures

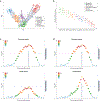

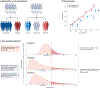
References
-
-
Martin AR et al. Clinical use of current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities. Nat. Genet 51, 584–591 (2019).
This paper demonstrates that PRSs have limited generalizability across populations and emphasizes the importance of diversity to realize the full and equitable potential of PRSs.
-
-
-
Fatumo S. et al. A roadmap to increase diversity in genomic studies. Nat. Med 28, 243–250 (2022).
This paper presents an updated ancestry tabulation for participants in GWAS catalogue and discusses strategies for increasing diversity in genomic studies.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 HG011717/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG006399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG012354/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA261339/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA246076/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011720/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM140487/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011723/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011710/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011715/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA241410/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG010480/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011697/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011719/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA249866/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States

