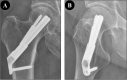
Prediction of hip joint function and analysis of risk factors for internal fixation failure after Femoral Neck System (FNS)
- PMID: 37620843
- PMCID: PMC10463719
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-023-06805-z
Prediction of hip joint function and analysis of risk factors for internal fixation failure after Femoral Neck System (FNS)
Abstract
Objective: Analysis of the risk factors affecting hip function and complications after femoral neck system (FNS) surgery for femoral neck fractures is of great significance for improving the procedure's efficacy.
Methods: The data of patients with femoral neck fractures who underwent FNS surgery in our hospital between October 2019 and October 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. Age, gender, time from injury to operation, fracture classification, operation time, fracture reduction, and postoperative weight-bearing time information were set as potential factors that may affect the results. Hip Harris scores were performed at 12 months postoperatively, and postoperative complication data (e.g., femoral head necrosis, nonunion, and femoral neck shortness) were collected. The risk factors affecting hip function and complications after FNS surgery were predicted using linear and logistic regression analyses.
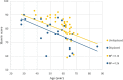
Results: A total of 69 cases of femoral neck fracture were included, with an average age of 56.09 ± 11.50 years. The linear analysis demonstrated that the age and fracture type of the patients were the risk factors affecting the Harris score of the hip joint after FNS surgery. Older patients with displaced femoral neck fractures had an inferior postoperative hip function. In addition, fracture type, reduction of the femoral neck, and postoperative weight-bearing significantly impacted postoperative complications. Displaced fractures, negative fixation, and premature weight-bearing (< 6 weeks) were risk factors for postoperative complications. The Harris score of patients with a shortened femoral neck in the included cases was not significantly different from that of patients without shortening (P = 0.25).
Conclusions: Advanced age and fracture type are important evaluation indicators of the Harris score after FNS internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in young patients. Fracture type, fracture reduction, and postoperative weight-bearing time are risk factors for complications after FNS.
Keywords: Femoral Neck System; Femoral neck fractures; Hip joint function; Internal fixation failure; Shortened femoral neck.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fracture classification and coronal plane position of bolt may affect the prognosis after femoral neck system (FNS) surgery for femoral neck fractures.BMC Surg. 2024 Dec 23;24(1):411. doi: 10.1186/s12893-024-02692-w. BMC Surg. 2024. PMID: 39710644 Free PMC article.
-
[Short term follow-up of unstable femoral neck fractures in young adults treated with femoral neck system and cannulated compression screws].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2023 Jul 25;36(7):635-40. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2023.07.008. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2023. PMID: 37475627 Chinese.
-
[Comparison of effectiveness of femoral neck system and cannulate compression screw in treatment of femoral neck fracture in young and middle-aged patients].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Oct 15;35(10):1286-1292. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202103099. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34651482 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Comparison of young femoral neck fractures treated by femoral neck system, multiple cancellous screws and dynamic hip screws: a retrospectively comparison study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Mar 2;25(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07319-y. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38431562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Femoral neck system vs. cannulated screws on treating femoral neck fracture: a meta-analysis and system review.Front Surg. 2023 Jul 18;10:1224559. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1224559. eCollection 2023. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 37533744 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biomechanical effects of FNS on femoral neck fractures based on different reduction quality: finite element analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Nov 15;25(1):914. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-08041-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39548463 Free PMC article.
-
Fracture classification and coronal plane position of bolt may affect the prognosis after femoral neck system (FNS) surgery for femoral neck fractures.BMC Surg. 2024 Dec 23;24(1):411. doi: 10.1186/s12893-024-02692-w. BMC Surg. 2024. PMID: 39710644 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-sliding of the femoral neck system to prevent postoperative shortening of femoral neck fractures.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 3;10(7):e29187. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29187. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38601698 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Short-Term Outcomes of Femoral Neck System (FNS) and Cannulated Screw Fixation in Patients with Femoral Neck Fractures: A Multicenter Study.Clin Orthop Surg. 2024 Apr;16(2):184-193. doi: 10.4055/cios23190. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Clin Orthop Surg. 2024. PMID: 38562623 Free PMC article.
-
Femoral neck system versus cannulated screws combined with medial plate for femoral neck fractures in young and middle-aged patients: a prospective multicenter randomized controlled trial.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Jun 3;20(1):559. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05972-0. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40457366 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bartels S, Kristensen TB, Gjertsen JE, Frihagen F, Rogmark C, Dolatowski FC, et al. Total hip arthroplasty leads to Better results after low-energy displaced femoral Neck fracture in patients aged 55 to 70 years: a Randomized Controlled Multicenter Trial comparing internal fixation and total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104(15):1341–1351. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.21.01411. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical