Cell-free DNA 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is highly sensitive for MRD assessment in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 37620919
- PMCID: PMC10464230
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-023-01547-0
Cell-free DNA 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is highly sensitive for MRD assessment in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
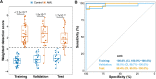
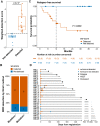
Measurable residual disease (MRD) is an important biomarker in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, MRD cannot be detected in many patients using current methods. We developed a highly sensitive 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) signature in cell-free DNA by analyzing 115 AML patients and 86 controls. The 5hmC method detected MRD in 20 of 29 patients with negative MRD by multiparameter flow cytometry and 11 of 14 patients with negative MRD by molecular methods. MRD detection by the 5hmC method was significantly associated with relapse-free survival. This novel method can be used in most AML patients and may significantly impact AML patient management.
Keywords: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine; Acute myeloid leukemia; Cell-free DNA; Measurable residual disease.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
C.H. is an inventor of the 5hmC-Seal method. All other authors declare no competing interests related to the work described.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cell-free DNA 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is an emerging marker of acute myeloid leukemia.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 20;12(1):12410. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16685-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35859008 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia by Cell-Free DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine.Genes (Basel). 2023 May 28;14(6):1180. doi: 10.3390/genes14061180. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372359 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of combined WT1 and multiparameter flow cytometry assessment for measurable residual disease after induction in non-APL acute myeloid leukemia.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2023 Sep;83(5):340-347. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2023.2227946. Epub 2023 Jun 24. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2023. PMID: 37355341
-
Prognostic and therapeutic implications of measurable residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Sep 3;14(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01148-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34479626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of multiparameter flow cytometry for detection of minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia.Am J Clin Pathol. 2009 Jan;131(1):16-26. doi: 10.1309/AJCP5TSD3DZXFLCX. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19095561 Review.
Cited by
-
T7 Endonuclease I-Mediated Single-Base Mismatch Biosensing Strategy for High-Resolution Quantitative Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Genomic DNA.JACS Au. 2025 Feb 17;5(3):1320-1327. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.4c01184. eCollection 2025 Mar 24. JACS Au. 2025. PMID: 40151246 Free PMC article.
-
5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Cell-Free DNA Predicts Immunotherapy Response in Lung Cancer.Cells. 2024 Apr 19;13(8):715. doi: 10.3390/cells13080715. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38667328 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Long-Term Plasma Storage on Cell-Free DNA Epigenetic Biomarker Studies.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 25;15(7):927. doi: 10.3390/biom15070927. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723799 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Free DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures for Lung Cancer Prognosis.Cells. 2024 Feb 6;13(4):298. doi: 10.3390/cells13040298. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38391911 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modifications of cfDNA in liquid biopsy for the cancer care continuum.Biomed J. 2025 Feb;48(1):100718. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2024.100718. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Biomed J. 2025. PMID: 38522508 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

