Muscle Thickness, Echo-Intensity, Peak Force, Time Under Tension, Total Load Lifted, and Perception of Effort Comparisons Between Two Abdominal Crunch Resistance Training Protocols in Recreationally-Trained Participants
- PMID: 37621710
- PMCID: PMC10446947
- DOI: 10.70252/BCSY3591
Muscle Thickness, Echo-Intensity, Peak Force, Time Under Tension, Total Load Lifted, and Perception of Effort Comparisons Between Two Abdominal Crunch Resistance Training Protocols in Recreationally-Trained Participants
Abstract
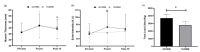
The primary purpose of this study was to evaluate acute dose response of different intensities with total volume equalized during the abdominal crunch exercise on muscle thickness, echo-intensity, peak force, time under tension, total load lifted, and perception of effort in recreationally-trained participants. Fifteen resistance-trained participants (23 ± 3 years) performed the abdominal crunch exercise in one of two different resistance training (RT) protocols in a randomized order: RT4×10RM (4 sets of 10RM / 1-min rest) or RT1×40RM (1 set of 40RM). Muscle thickness (MT), echo-intensity (EI), peak force (PF), time under tension (TUT), total load lifted (TLL), and session rating of perceived exertion (sRPE) were measured pre-test and post-test (0-min and 15-min). Two-way repeated-measures ANOVAs (2 × 3) were used to test differences between RT protocols (RT4×10RM and RT1×40RM) and time (pre-test, post-0, and post-15) for MT, EI, and PF. Paired t-test was used to compare RT protocols for sRPE, TLL, and TUT. For MT, there were significant differences for RT4×10RM between pre-x post-0 (p = 0.011), pre-x post-15 (p < 0.001), and post-0 × post-15 (p = 0.02); and for RT1×40RM between pre-x post-0 (p < 0.001) and pre-x post-15 (p = 0.003). For EI, there was a significant difference for RT4×10RM between pre-x post-0 (p = 0.002). For sRPE, there was no significant difference between RT protocols. For TLL and TUT, there were significant differences between RT protocols (p < 0.05). In conclusion, both RT protocols (RT4×10RM and RT1×40RM) induced similar increases in MT but not for EI. TLL and TUT were higher for RT4×10RM. PF and sRPE were similar between RT protocols.
Keywords: Strength; muscle pump; muscular performance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exercise Variability Did Not Affect Muscle Thickness and Peak Force for Elbow Flexors After a Resistance Training Session in Recreationally-Trained Subjects.Int J Exerc Sci. 2021 Nov 1;14(3):1294-1304. doi: 10.70252/XAFX1170. eCollection 2021. Int J Exerc Sci. 2021. PMID: 35096238 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Dose-Response of Duration During the Isometric Forearm Plank Exercise on Muscle Thickness, Echo-Intensity, Peak Force, and Perception of Effort in Recreationally-Trained Participants.Int J Exerc Sci. 2022 May 1;15(6):676-685. doi: 10.70252/RDKT2873. eCollection 2022. Int J Exerc Sci. 2022. PMID: 35991937 Free PMC article.
-
Seated row and biceps curl exercises present similar acute responses on muscle thickness, arm circumference, and peak force for elbow flexors after a resistance training session in recreationally-trained subjects.J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2020 Nov;60(11):1415-1422. doi: 10.23736/S0022-4707.20.10996-4. Epub 2020 Jun 23. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2020. PMID: 32586082
-
Dynamic training volume: a construct of both time under tension and volume load.J Sports Sci Med. 2006 Dec 15;5(4):707-13. eCollection 2006. J Sports Sci Med. 2006. PMID: 24357968 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay between internal and external load parameters during different strength training sessions in resistance-trained men.Eur J Sport Sci. 2021 Jan;21(1):16-25. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2020.1725646. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Eur J Sport Sci. 2021. PMID: 32008472
References
-
- Anderson EA, Nilson J, Thorsthensson A. Abdominal and hip flexor muscle activation during various training exercises. Eur J Appl Physiol. 1997;75:115–123. - PubMed
-
- Burd NA, Andrews RJ, West DW, Little JP, Cochran AJ, Hector AJ, Cashaback JG, Gibala MJ, Potvin JR, Baker SK, Phillips SM. Muscle time under tension during resistance exercise stimulates differential muscle protein sub-fractional synthetic responses in men. J Physiol. 2012;590(2):351–362. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen YL, Wolin MS, Messina EJ. Evidence for cgmp mediation of skeletal muscle arteriolar dilation to lactate. J Appl Physiol. 1996;81(1):349–354. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
