Impact of HIF1-α/TGF-β/Smad-2/Bax/Bcl2 pathways on cobalt chloride-induced cardiac and hepatorenal dysfunction
- PMID: 37621844
- PMCID: PMC10445593
- DOI: 10.2144/fsoa-2023-0050
Impact of HIF1-α/TGF-β/Smad-2/Bax/Bcl2 pathways on cobalt chloride-induced cardiac and hepatorenal dysfunction
Abstract
Background: Cobalt chloride (CoCl2) is a ferromagnetic ubiquitous trace element extensively dispersed in the environment. Nevertheless, it may merit human hazard.
Aim: Excess cobalt can harm vital organs this paves the way to elucidate the toxic impact of CoCl2 on the liver, kidney and heart.
Method: CoCl2 was injected in a dose of (60 mg/kg, S.C.) proceeded via Carnosine (200 mg/kg) and/or Arginine (200 mg/kg) treatment 1 month, 24 and 1 h, prior to CoCl2-intoxication.
Results: CoCl2 significantly alleviated hemoglobin concentration and BCl2; meanwhile, protein expression of transforming growth factor (TGF-β), hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α), Mothers against decapentaplegic (Smad-2), AKT protein expression and Bax/Bcl2 ratio was noticeably elevated.
Conclusion: The combination of the aforementioned antioxidants exerted a synergistic anti-apoptotic impact in all target tissues.
Keywords: AKT; Bax/Bcl2 ratio; HIF1-α; Smad-2; TGF-β; cobalt chloride.
Plain language summary
Cobalt chloride (CoCl2) is commonly found in the environment and used in medicine. However, it can be harmful to our health, particularly when consumed in excessive amounts, leading to damage in important organs. Therefore, we investigated the toxic effects of CoCl2 on the liver, kidney, and heart. We also explored potential treatments using substances like Carnosine and Arginine. We discovered that Arginine and carnosine had a positive effect on certain factors related to the health of the organs. They helped regulate the levels of hemoglobin and BCl2, as well as the expression of proteins such as transforming growth factor (TGF-β), hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α), Mothers against decapentaplegic (Smad-2), AKT, and apoptotic biomarkers like the Bax/Bcl2 ratio. When these antioxidants were combined, they had a stronger protective effect against cell death and mutations in all the organs studied.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest disclosure The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest present.
Figures

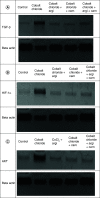



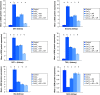


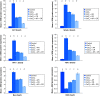
References
-
- Ajibade AJ, Ogunmola IA, Okeleye AE. Ameliorative Effects of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract on the Cobalt Chloride-Induced Liver Damage in Adult Wistar Rats. Sys. Rev. Pharm. 12(12), 3865–3871 (2021).
-
- Karakka Kal AK, Perwad Z, Karatt TK, Nalakath J, Subhahar M. Using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry to assess essential and performance-enhancing metals in the urine of racehorses. J. Anal. Toxicol. 44(5), 490–498 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Chen RJ, Lee VR. Cobalt Toxicity. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, FL, USA: (2022). PMID: 36508548. - PubMed
-
- Mohamed AA, Metwally MM, Khalil SR, Salem GA, Ali HA. Moringa oleifera extract attenuates the CoCl2 induced hypoxia of rat's brain: expression pattern of HIF-1α, NF-kB, MAO and EPO. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 109, 1688–1697 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Oyagbemi AA, Ajibade TO, Esan OO et al. Naringin abrogates angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) activity and podocin signaling pathway in cobalt chloride-induced nephrotoxicity and hypertension. Biomarkers. 28(2), 206–216 (2022). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
