Revisiting the Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles: Uncovering Influences of Plant Extracts as Reducing Agents for Enhanced Synthesis Efficiency and Its Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 37621852
- PMCID: PMC10444627
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S419369
Revisiting the Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles: Uncovering Influences of Plant Extracts as Reducing Agents for Enhanced Synthesis Efficiency and Its Biomedical Applications
Abstract
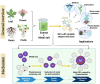
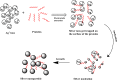
Background: Conventional nanoparticle synthesis methods involve harsh conditions, high costs, and environmental pollution. In this context, researchers are actively searching for sustainable, eco-friendly alternatives to conventional chemical synthesis methods. This has led to the development of green synthesis procedures among which the exploration of the plant-mediated synthesis of nanoparticles experienced a great development. Especially, because plant extracts can work as reducing and stabilizing agents. This opens up new possibilities for cost-effective, environmentally-friendly nanoparticle synthesis with enhanced size uniformity and stability. Moreover, bio-inspired nanoparticles derived from plants exhibit intriguing pharmacological properties, making them highly promising for use in medical applications due to their biocompatibility and nano-dimension.
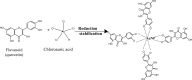
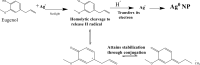
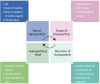
Objective: This study investigates the role of specific phytochemicals, such as phenolic compounds, terpenoids, and proteins, in plant-mediated nanoparticle synthesis together with their influence on particle size, stability, and properties. Additionally, we highlight the potential applications of these bio-derived nanoparticles, particularly with regard to drug delivery, disease management, agriculture, bioremediation, and application in other industries.
Methodology: Extensive research on scientific databases identified green synthesis methods, specifically plant-mediated synthesis, with a focus on understanding the contributions of phytochemicals like phenolic compounds, terpenoids, and proteins. The database search covered the field's development over the past 15 years.
Results: Insights gained from this exploration highlight plant-mediated green synthesis for cost-effective nanoparticle production with significant pharmacological properties. Utilizing renewable biological resources and controlling nanoparticle characteristics through biomolecule interactions offer promising avenues for future research and applications.
Conclusion: This review delves into the scientific intricacies of plant-mediated synthesis of nanoparticles, highlighting the advantages of this approach over the traditional chemical synthesis methods. The study showcases the immense potential of green synthesis for medical and other applications, aiming to inspire further research in this exciting area and promote a more sustainable future.
Keywords: biocompatibility; biomedical application; green synthesis; medicinal plants; nanomaterials; surface functionalization.
© 2023 Singh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
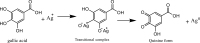


Similar articles
-
Utilizing Plant Phytoconstituents in Metal Oxide Nanoparticle Synthesis for Cancer Therapies.Curr Pharm Des. 2025;31(16):1270-1289. doi: 10.2174/0113816128329342241120105041. Curr Pharm Des. 2025. PMID: 39781736 Review.
-
Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts as Beneficial Prospect for Cancer Theranostics.Molecules. 2021 Oct 22;26(21):6389. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216389. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant-mediated green synthesis of metal-based nanoparticles for dermopharmaceutical and cosmetic applications.Int J Pharm. 2021 Mar 15;597:120311. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120311. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Int J Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33539998 Review.
-
Green approaches for the synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles using microbial and plant extracts.Nanoscale. 2022 Feb 17;14(7):2534-2571. doi: 10.1039/d1nr08144f. Nanoscale. 2022. PMID: 35133391 Review.
-
Metal-plant frameworks in nanotechnology: An overview.Phytomedicine. 2018 Nov 15;50:148-156. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2017.08.025. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30466973 Review.
Cited by
-
Green Synthesis of Silver Oxide Nanoparticles from Mauritia flexuosa Fruit Extract: Characterization and Bioactivity Assessment.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Nov 22;14(23):1875. doi: 10.3390/nano14231875. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39683263 Free PMC article.
-
Bionanotechnology: A Paradigm for Advancing Environmental Sustainability.Indian J Microbiol. 2025 Mar;65(1):306-332. doi: 10.1007/s12088-024-01389-1. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Indian J Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40371027
-
Unveiling the dynamic trends of plant-derived exosome nanovesicles-based theranostics: through bibliometric and visualized analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 24;12:1553915. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1553915. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40630491 Free PMC article.
-
Green-synthesized metal nanoparticles: a promising approach for accelerated wound healing.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 16;13:1637589. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1637589. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40741533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green synthesis of Mn-doped iron oxide nanoparticles using sugarcane juice for magnetic hyperthermia applications.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 6;15(1):28686. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11998-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40770212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El-Shafai N, El-Khouly ME, El-Kemary M, Ramadan M, Eldesoukey I, Masoud M. Graphene oxide decorated with zinc oxide nanoflower, silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles: fabrication, characterization, DNA interaction, and antibacterial activity. RSC Adv. 2019;9(7):3704–3714. doi:10.1039/c8ra09788g - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- EL-Sheshtawy HS, El-Hosainy HM, Shoueir KR, El-Mehasseb IM, El-Kemary M. Facile immobilization of Ag nanoparticles on g-C3N4/V2O5 surface for enhancement of post-illumination, catalytic, and photocatalytic activity removal of organic and inorganic pollutants. Appl Surf Sci. 2019;467:268–276. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.109 - DOI
-
- Kaviya S. Synthesis, self-assembly, sensing methods and mechanism of bio-source facilitated nanomaterials: a review with future outlook. Nano Struct Nano Objects. 2020;23:100498. doi:10.1016/j.nanoso.2020.100498 - DOI
-
- Al-Anssari S, Ali M, Alajmi M, et al. Synergistic Effect of Nanoparticles and Polymers on the Rheological Properties of Injection Fluids: Implications for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Energy Fuels. 2021;35(7):6125–6135. doi:10.1021/acs.energyfuels.1c00105/asset/images/medium/ef1c00105_0011.gif - DOI
-
- Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I. Nanoparticles: properties, applications and toxicities. Arab J Chem. 2019;12(7):908–931. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

