Excitatory/inhibitory balance emerges as a key factor for RBN performance, overriding attractor dynamics
- PMID: 37621962
- PMCID: PMC10445160
- DOI: 10.3389/fncom.2023.1223258
Excitatory/inhibitory balance emerges as a key factor for RBN performance, overriding attractor dynamics
Abstract
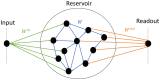
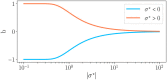
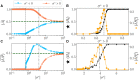
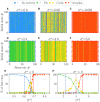
Reservoir computing provides a time and cost-efficient alternative to traditional learning methods. Critical regimes, known as the "edge of chaos," have been found to optimize computational performance in binary neural networks. However, little attention has been devoted to studying reservoir-to-reservoir variability when investigating the link between connectivity, dynamics, and performance. As physical reservoir computers become more prevalent, developing a systematic approach to network design is crucial. In this article, we examine Random Boolean Networks (RBNs) and demonstrate that specific distribution parameters can lead to diverse dynamics near critical points. We identify distinct dynamical attractors and quantify their statistics, revealing that most reservoirs possess a dominant attractor. We then evaluate performance in two challenging tasks, memorization and prediction, and find that a positive excitatory balance produces a critical point with higher memory performance. In comparison, a negative inhibitory balance delivers another critical point with better prediction performance. Interestingly, we show that the intrinsic attractor dynamics have little influence on performance in either case.
Keywords: RBN; attractor; criticality; memory; prediction; reservoir computing.
Copyright © 2023 Calvet, Rouat and Reulet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Alexandre L. A., Embrechts M. J., Linton J. (2009). “Benchmarking reservoir computing on time-independent classification tasks,” in Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks 89–93. 10.1109/IJCNN.2009.5178920 - DOI
-
- Balafrej I., Alibart F., Rouat J. (2022). P-CRITICAL: a reservoir autoregulation plasticity rule for neuromorphic hardware. Neuromor. Comput. Eng. 2, 024007. 10.1088/2634-4386/ac6533 - DOI
-
- Benjamin B. V., Gao P., McQuinn E., Choudhary S., Chandrasekaran A. R., Bussat J.-M., et al. . (2014). Neurogrid: a mixed-analog-digital multichip system for large-scale neural simulations. Proc. IEEE 102, 699–716. 10.1109/JPROC.2014.2313565 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

