A Tissue Systems Pathology Test Outperforms the Standard-of-Care Variables in Predicting Progression in Patients With Barrett's Esophagus
- PMID: 37622544
- PMCID: PMC10684217
- DOI: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000631
A Tissue Systems Pathology Test Outperforms the Standard-of-Care Variables in Predicting Progression in Patients With Barrett's Esophagus
Abstract
Introduction: Objective risk stratification is needed for patients with Barrett's esophagus (BE) to enable risk-aligned management to improve health outcomes. This study evaluated the predictive performance of a tissue systems pathology [TSP-9] test (TissueCypher) vs current clinicopathologic variables in a multicenter cohort of patients with BE.
Methods: Data from 699 patients with BE from 5 published studies on the TSP-9 test were evaluated. Five hundred nine patients did not progress during surveillance, 40 were diagnosed with high-grade dysplasia/esophageal adenocarcinoma (HGD/EAC) within 12 months, and 150 progressed to HGD/EAC after 12 months. Age, sex, segment length, hiatal hernia, original and expert pathology review diagnoses, and TSP-9 risk classes were collected. The predictive performance of clinicopathologic variables and the TSP-9 test was compared, and the TSP-9 test was evaluated in clinically relevant patient subsets.
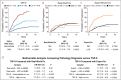
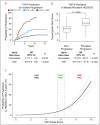
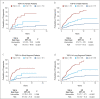
Results: The sensitivity of the TSP-9 test in detecting progressors was 62.3% compared with 28.3% for expert-confirmed low-grade dysplasia (LGD), while the original diagnosis abstracted from medical records did not provide any significant risk stratification. The TSP-9 test identified 57% of progressors with nondysplastic Barrett's esophagus (NDBE) ( P < 0.0001). Patients with NDBE who scored TSP-9 high risk progressed at a similar rate (3.2%/yr) to patients with expert-confirmed LGD (3.7%/yr). The TSP-9 test provided significant risk stratification in clinically low-risk patients (NDBE, female, short-segment BE) and clinically high-risk patients (IND/LGD, male, long-segment BE) ( P < 0.0001 for comparison of high-risk classes vs low-risk classes).
Discussion: The TSP-9 test predicts risk of progression to HGD/EAC independently of current clinicopathologic variables in patients with BE. The test provides objective risk stratification results that may guide management decisions to improve health outcomes for patients with BE.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Qumseya B, Sultan S, Bain P, et al. ASGE guideline on screening and surveillance of Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2019;90(3):335–59.e2. - PubMed
-
- Kastelein F, van Olphen SH, Steyerberg EW, et al. . Impact of surveillance for Barrett's oesophagus on tumour stage and survival of patients with neoplastic progression. Gut 2016;65(4):548–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

