Pathomechanistic Networks of Motor System Injury in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- PMID: 37622689
- PMCID: PMC11284732
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X21666230824091601
Pathomechanistic Networks of Motor System Injury in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is the most common, adult-onset, progressive motor neurodegenerative disorder that results in death within 3 years of the clinical diagnosis. Due to the clinicopathological heterogeneity, any reliable biomarkers for diagnosis or prognosis of ALS have not been identified till date. Moreover, the only three clinically approved treatments are not uniformly effective in slowing the disease progression. Over the last 15 years, there has been a rapid advancement in research on the complex pathomechanistic landscape of ALS that has opened up new avenues for successful clinical translation of targeted therapeutics. Multiple studies suggest that the age-dependent interaction of risk-associated genes with environmental factors and endogenous modifiers is critical to the multi-step process of ALS pathogenesis. In this review, we provide an updated discussion on the dysregulated cross-talk between intracellular homeostasis processes, the unique molecular networks across selectively vulnerable cell types, and the multisystemic nature of ALS pathomechanisms. Importantly, this work highlights the alteration in epigenetic and epitranscriptomic landscape due to gene-environment interactions, which have been largely overlooked in the context of ALS pathology. Finally, we suggest that precision medicine research in ALS will be largely benefitted from the stratification of patient groups based on the clinical phenotype, onset and progression, genome, exposome, and metabolic identities.
Keywords: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); RNA modification.; epigenetics; gene environment interaction; heterogeneity; metabolism; motor neuron disease; pathophysiology.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures

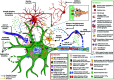
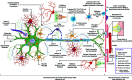




References
-
- Checkoway H., Lundin J.I., Kelada S.N. Neurodegenerative diseases. IARC Sci. Publ. 2011;(163):407–419. - PubMed
-
- Logroscino G., Piccininni M., Marin B., Nichols E., Abd-Allah F., Abdelalim A., Alahdab F., Asgedom S.W., Awasthi A., Chaiah Y., Daryani A., Do H.P., Dubey M., Elbaz A., Eskandarieh S., Farhadi F., Farzadfar F., Fereshtehnejad S-M., Fernandes E., Filip I., Foreman K.J., Gebre A.K., Gnedovskaya E.V., Hamidi S., Hay S.I., Irvani S.S.N., Ji J.S., Kasaeian A., Kim Y.J., Mantovani L.G., Mashamba-Thompson T.P., Mehndiratta M.M., Mokdad A.H., Nagel G., Nguyen T.H., Nixon M.R., Olagunju A.T., Owolabi M.O., Piradov M.A., Qorbani M., Radfar A., Reiner R.C., Sahraian M.A., Sarvi S., Sharif M., Temsah O., Tran B.X., Truong N.T., Venketasubramanian N., Winkler A.S., Yimer E.M., Feigin V.L., Vos T., Murray C.J.L. Global, regional, and national burden of motor neuron diseases 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(12):1083–1097. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30404-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

