Unique epitope-antibody interactions in the intrinsically disordered proteoglycan-like domain of human carbonic anhydrase IX defined by high-resolution NMR combined with yeast surface display
- PMID: 37622732
- PMCID: PMC10461516
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2023.2248672
Unique epitope-antibody interactions in the intrinsically disordered proteoglycan-like domain of human carbonic anhydrase IX defined by high-resolution NMR combined with yeast surface display
Abstract
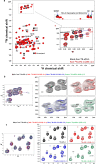
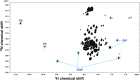
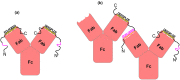
Carbonic anhydrase (CA)-IX is an extracellular enzyme that is essential in the adaptation of tumor cells to their increasingly more hypoxic and acidic microenvironment. Within the family of carbonic anhydrases, CA-IX is unique in that it is the only CA with an N-terminal intrinsically disordered region (IDR) containing a proteoglycan (PG)-like domain. This PG-like IDR has been described to be instrumental in CA-IX's enzyme activity, as well as tumor cell motility and invasion. We have characterized the antibody-epitope interactions of two novel and unique antibodies (11H9 and 12H8) that are specific for the human CA-IX's IDR. Binding interactions of these antibodies to the intact IDR were studied by surface plasmon resonance and high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, while the specific epitopes were determined by both NMR and yeast surface display (YSD). Our data show that 12H8 binds to the N-terminus of CA-IX, while 11H9 has a high affinity for an epitope located in the central region of the IDR containing three GEEDLP repeats in a manner that is different from the previously described M75 antibody. Titration NMR spectroscopy using CA-IX's entire IDR in addition identified a secondary epitope of 11H9 at the beginning of the PG-like domain that remains exposed and available for further binding events after the engagement at its primary epitope at the center of the PG-like domain. Transverse relaxation optimized NMR spectroscopy of 11H9-F(Ab) in complex with the CA-IX IDR outlines structural rigidification of a linear epitope, while the rest of the IDR remains largely unstructured upon complex formation. This study illustrates how high-resolution NMR and YSD are used as complementary tools for a comprehensive characterization of antibody-epitope interactions involving intrinsically unstructured antigen domains with highly repetitive sequences.
Keywords: Antibodies; F(ab); NMR spectroscopy; antibody–antigen interactions; carbonic anhydrase IX; epitope mapping; intrinsically disordered proteins; yeast surface display.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Monoclonal antibodies generated in carbonic anhydrase IX-deficient mice recognize different domains of tumour-associated hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrase IX.J Immunol Methods. 2003 Nov;282(1-2):117-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2003.08.011. J Immunol Methods. 2003. PMID: 14604546
-
Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX) mediates tumor cell interactions with microenvironment.Oncol Rep. 2005 May;13(5):977-82. Oncol Rep. 2005. PMID: 15809767
-
Stabilization of antibody structure upon association to a human carbonic anhydrase IX epitope studied by X-ray crystallography, microcalorimetry, and molecular dynamics simulations.Proteins. 2008 May 15;71(3):1275-87. doi: 10.1002/prot.21821. Proteins. 2008. PMID: 18041760
-
Intrinsically disordered features of carbonic anhydrase IX proteoglycan-like domain.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Mar;78(5):2059-2067. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03697-3. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33201250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbonic anhydrase IX: Biochemical and crystallographic characterization of a novel antitumor target.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Feb;1804(2):404-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.07.027. Epub 2009 Aug 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19679200 Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the assembly mechanism of SADS-CoV virus nucleocapsid protein: insights from RNA binding, dimerization, and epitope diversity profiling.J Virol. 2024 Aug 20;98(8):e0092624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00926-24. Epub 2024 Jul 31. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39082816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ihnatko R, Kubes M, Takacova M, Sedlakova O, Sedlak J, Pastorek J, Kopacek J, Pastorekova S. Extracellular acidosis elevates carbonic anhydrase IX in human glioblastoma cells via transcriptional modulation that does not depend on hypoxia. Int J Oncol. 2006;29:1025–33. PMID: 16964400 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16964400. - PubMed
-
- Andreucci E, Peppicelli S, Carta F, Brisotto G, Biscontin E, Ruzzolini J, Bianchini F, Biagioni A, Supuran CT, Calorini L. Carbonic anhydrase IX inhibition affects viability of cancer cells adapted to extracellular acidosis. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017;95:1341–53. doi:10.1007/s00109-017-1590-9. PMID: 28929255. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
