Development and Evaluation of a Flexible PVDF-Based Balloon Sensor for Detecting Mechanical Forces at Key Esophageal Nodes in Esophageal Motility Disorders
- PMID: 37622877
- PMCID: PMC10452430
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13080791
Development and Evaluation of a Flexible PVDF-Based Balloon Sensor for Detecting Mechanical Forces at Key Esophageal Nodes in Esophageal Motility Disorders
Abstract
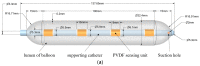
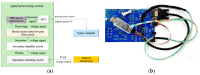
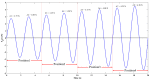
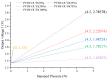
Prevailing methods for esophageal motility assessments, such as perfusion manometry and probe-based function imaging, frequently overlook the intricate stress fields acting on the liquid-filled balloons at the forefront of the probing device within the esophageal lumen. To bridge this knowledge gap, we innovatively devised an infusible flexible balloon catheter, equipped with a quartet of PVDF piezoelectric sensors. This design, working in concert with a bespoke local key-node analytical algorithm and a sensor array state analysis model, seeks to shed new light on the dynamic mechanical characteristics at pivotal esophageal locales. To further this endeavor, we pioneered a singular closed balloon system and a complementary signal acquisition and processing system that employs a homogeneously distributed PVDF piezoelectric sensor array for the real-time monitoring of dynamic mechanical nuances in the esophageal segment. An advanced analytical model was established to scrutinize the coupled physical fields under varying degrees of balloon inflation, thereby facilitating a thorough dynamic stress examination of local esophageal nodes. Our rigorous execution of static, dynamic, and simulated swallowing experiments robustly substantiated the viability of our design, the logical coherence of our esophageal key-point stress analytical algorithm, and the potential clinical utility of a flexible esophageal key-node stress detection balloon probe outfitted with a PVDF array. This study offers a fresh lens through which esophageal motility testing can be viewed and improved upon.
Keywords: advanced infusion-compatible balloon catheter; esophageal biomechanical dynamics; esophageal stress analysis; polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) piezoelectric sensor matrix.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Balloon sensors for the manometric recording of the pharyngoesophageal tract: an experimental study.Dysphagia. 2003 Fall;18(4):249-54. doi: 10.1007/s00455-003-0009-7. Dysphagia. 2003. PMID: 14571328
-
The Structure Design of Piezoelectric Poly(vinylidene Fluoride) (PVDF) Polymer-Based Sensor Patch for the Respiration Monitoring under Dynamic Walking Conditions.Sensors (Basel). 2015 Jul 31;15(8):18801-12. doi: 10.3390/s150818801. Sensors (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26263992 Free PMC article.
-
A PVDF-Based Sensor for Internal Stress Monitoring of a Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular (CFST) Column Subject to Impact Loads.Sensors (Basel). 2018 May 23;18(6):1682. doi: 10.3390/s18061682. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29882909 Free PMC article.
-
Future prospects and recent developments of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) piezoelectric polymer; fabrication methods, structure, and electro-mechanical properties.RSC Adv. 2023 Jan 9;13(1):370-387. doi: 10.1039/d2ra06774a. eCollection 2022 Dec 19. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36683768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrospun PVDF-based piezoelectric nanofibers: materials, structures, and applications.Nanoscale Adv. 2023 Jan 19;5(4):1043-1059. doi: 10.1039/d2na00773h. eCollection 2023 Feb 14. Nanoscale Adv. 2023. PMID: 36798499 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Development of a balloon sensor device for force-electrical coupling measurement of esophagus].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Jun 25;42(3):610-619. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202404019. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40566785 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Yadlapati R., Kahrilas P.J., Fox M.R., Bredenoord A.J., Gyawaliet C.P., Roman S., Babaei A., Mittal R.K., Rommel N., Savarino E., et al. Esophageal motility disorders on high-resolution manometry: Chicago classification version 4.0. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021;33:e14058. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14058. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Savarino E., Marabotto E., Bodini G., Furnari M., Della Coletta M., Ghisa M., Barberio B., Frazzoni M., De Bortoli N., Zentilin P., et al. Advancements in the use of manometry and impedance testing for esophageal functional disorders. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019;13:425–435. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2019.1595587. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tutuian R. Impedance technology for the management of esophageal disorders. Eur. Surg. 2008;40:50–57. doi: 10.1007/s10353-008-0393-1. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

