Recent Advances in DNA Nanotechnology-Enabled Biosensors for Virus Detection
- PMID: 37622908
- PMCID: PMC10452139
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13080822
Recent Advances in DNA Nanotechnology-Enabled Biosensors for Virus Detection
Abstract
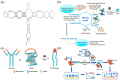
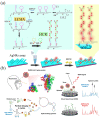
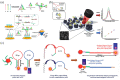
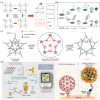
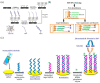
Virus-related infectious diseases are serious threats to humans, which makes virus detection of great importance. Traditional virus-detection methods usually suffer from low sensitivity and specificity, are time-consuming, have a high cost, etc. Recently, DNA biosensors based on DNA nanotechnology have shown great potential in virus detection. DNA nanotechnology, specifically DNA tiles and DNA aptamers, has achieved atomic precision in nanostructure construction. Exploiting the programmable nature of DNA nanostructures, researchers have developed DNA nanobiosensors that outperform traditional virus-detection methods. This paper reviews the history of DNA tiles and DNA aptamers, and it briefly describes the Baltimore classification of virology. Moreover, the advance of virus detection by using DNA nanobiosensors is discussed in detail and compared with traditional virus-detection methods. Finally, challenges faced by DNA nanobiosensors in virus detection are summarized, and a perspective on the future development of DNA nanobiosensors in virus detection is also provided.
Keywords: DNA nanotechnology; DNA origami; DNA tile; biosensors; virus detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Building DNA nanostructures for molecular computation, templated assembly, and biological applications.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Jun 17;47(6):1778-88. doi: 10.1021/ar500023b. Epub 2014 Apr 10. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 24720350
-
Aptamers as molecular recognition elements for electrical nanobiosensors.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008 Feb;390(4):1023-32. doi: 10.1007/s00216-007-1643-y. Epub 2007 Oct 23. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008. PMID: 17955221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mix-and-match nanobiosensor design: Logical and spatial programming of biosensors using self-assembled DNA nanostructures.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2018 Nov;10(6):e1518. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1518. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29633568 Review.
-
Cancer diagnosis using nanomaterials based electrochemical nanobiosensors.Biosens Bioelectron. 2019 Feb 1;126:773-784. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.11.026. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019. PMID: 30554099 Review.
-
Recent Advances in DNA Nanotechnology for Plasmonic Biosensor Construction.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 15;12(6):418. doi: 10.3390/bios12060418. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35735565 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanotechnology's Applications and Potential in Various Fields.Cureus. 2024 Apr 28;16(4):e59234. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59234. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38813303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies and Recent Advances on Improving Efficient Antitumor of Lenvatinib Based on Nanoparticle Delivery System.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jun 10;19:5581-5603. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S460844. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38882543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid diagnosis of ocular viral infections via single-virus detection using solid-state nanopore: A diagnostic evaluation study.PNAS Nexus. 2025 May 21;4(6):pgaf161. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf161. eCollection 2025 Jun. PNAS Nexus. 2025. PMID: 40496189 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in graphene-based electroanalytical devices for healthcare applications.Nanoscale. 2024 Jul 11;16(27):12857-12882. doi: 10.1039/d3nr06137j. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 38888429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology's frontier in combatting infectious and inflammatory diseases: prevention and treatment.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Feb 21;9(1):34. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01745-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38378653 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smyrlaki I., Ekman M., Lentini A., de Sousa N.R., Papanicolaou N., Vondracek M., Aarum J., Safari H., Muradrasoli S., Rothfuchs A.G., et al. Massive and Rapid COVID-19 Testing Is Feasible by Extraction-Free SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:4812. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18611-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

