Bridging Locomotion and Manipulation Using Reconfigurable Robotic Limbs via Reinforcement Learning
- PMID: 37622969
- PMCID: PMC10452096
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics8040364
Bridging Locomotion and Manipulation Using Reconfigurable Robotic Limbs via Reinforcement Learning
Abstract
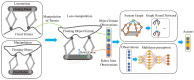
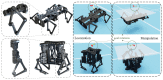
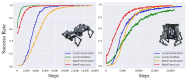
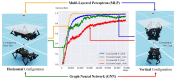
Locomotion and manipulation are two essential skills in robotics but are often divided or decoupled into two separate problems. It is widely accepted that the topological duality between multi-legged locomotion and multi-fingered manipulation shares an intrinsic model. However, a lack of research remains to identify the data-driven evidence for further research. This paper explores a unified formulation of the loco-manipulation problem using reinforcement learning (RL) by reconfiguring robotic limbs with an overconstrained design into multi-legged and multi-fingered robots. Such design reconfiguration allows for adopting a co-training architecture for reinforcement learning towards a unified loco-manipulation policy. As a result, we find data-driven evidence to support the transferability between locomotion and manipulation skills using a single RL policy with a multilayer perceptron or graph neural network. We also demonstrate the Sim2Real transfer of the learned loco-manipulation skills in a robotic prototype. This work expands the knowledge frontiers on loco-manipulation transferability with learning-based evidence applied in a novel platform with overconstrained robotic limbs.
Keywords: loco-manipulation; reconfigurable robot; reinforcement learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dexterous Manipulation for Multi-Fingered Robotic Hands With Reinforcement Learning: A Review.Front Neurorobot. 2022 Apr 25;16:861825. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2022.861825. eCollection 2022. Front Neurorobot. 2022. PMID: 35548780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-expert synthesis for versatile locomotion and manipulation skills.Front Robot AI. 2022 Sep 28;9:970890. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2022.970890. eCollection 2022. Front Robot AI. 2022. PMID: 36246489 Free PMC article.
-
Variational Information Bottleneck Regularized Deep Reinforcement Learning for Efficient Robotic Skill Adaptation.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 9;23(2):762. doi: 10.3390/s23020762. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679561 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling and Control of a Reconfigurable Robot for Achieving Reconfiguration and Locomotion with Different Shapes.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Aug 9;21(16):5362. doi: 10.3390/s21165362. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34450805 Free PMC article.
-
A Survey on Deep Reinforcement Learning Algorithms for Robotic Manipulation.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Apr 5;23(7):3762. doi: 10.3390/s23073762. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37050822 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Leveraging imitation learning in agricultural robotics: a comprehensive survey and comparative analysis.Front Robot AI. 2024 Oct 17;11:1441312. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2024.1441312. eCollection 2024. Front Robot AI. 2024. PMID: 39483488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing the Efficiency of a Cybersecurity Operations Center Using Biomimetic Algorithms Empowered by Deep Q-Learning.Biomimetics (Basel). 2024 May 21;9(6):307. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9060307. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38921187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Billeschou P., Bijma N.N., Larsen L.B., Gorb S.N., Larsen J.C., Manoonpong P. Framework for Developing Bio-Inspired Morphologies for Walking Robots. Appl. Sci. 2020;10:6986. doi: 10.3390/app10196986. - DOI
-
- Shi F., Homberger T., Lee J., Miki T., Zhao M., Farshidian F., Okada K., Inaba M., Hutter M. Circus ANYmal: A Quadruped Learning Dexterous Manipulation with its Limbs; Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA); Xi’an, China. 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 2316–2323.
-
- Lynch K.M. Ph.D. Thesis. Carnegie Mellon University; Pittsburgh, PA, USA: 1996. Nonprehensile Robotic Manipulation: Controllability and Planning.
-
- Johnson A.M., Koditschek D.E. Legged Self-Manipulation. IEEE Access. 2013;1:310–334. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2013.2263192. - DOI
-
- Mason M.T. Toward Robotic Manipulation. Annu. Rev. Control. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2018;1:1–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev-control-060117-104848. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 62206119/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- JCYJ20220818100417038/Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission
- ZDSYS20220527171403009/Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission
- N.A./Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Human Augmentation and Rehabilitation Robotics in Universities
- N.A./SUSTech-MIT Joint Centers for Mechanical Engineering Research and Education
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

