Bigels as Delivery Systems: Potential Uses and Applicability in Food
- PMID: 37623103
- PMCID: PMC10453560
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9080648
Bigels as Delivery Systems: Potential Uses and Applicability in Food
Abstract
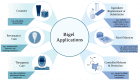
Bigels have been mainly applied in the pharmaceutical sector for the controlled release of drugs or therapeutics. However, these systems, with their intricate structures, hold great promise for wider application in food products. Besides their classical role as carrier and target delivery vehicles for molecules of interest, bigels may also be valuable tools for building complex food structures. In the context of reducing or even eliminating undesirable (but often highly functional) food components, current strategies often critically affect food structure and palatability. The production of solid fat systems that are trans-fat-free and have high levels of unsaturated fatty acids is one of the challenges the food industry currently faces. According to recent studies, bigels can be successfully used as ingredients for total or partial solid fat replacement in complex food matrices. This review aims to critically assess current research on bigels in food and pharmaceutical applications, discuss the role of bigel composition and production parameters on the characteristics of bigels and further expand the use of bigels as solid fat replacers and functional food ingredients. The hydrogel:oleogel ratio, selected gelators, inclusion of surfactants and encapsulation of molecules of interest, and process parameters (e.g., temperature, shear rate) during bigel production play a crucial role in the bigel's rheological and textural properties, microstructure, release characteristics, biocompatibility, and stability. Besides exploring the role of these parameters in bigel production, future research directions for bigels in a food context are explored.
Keywords: bigels; controlled release; food; hydrogels; organogels; solid fat replacement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Investigating the Influence of Hydrogel and Oleogel Ratios on Physico Chemical Characteristics, Microstructure, Rheology, and Texture of a Food Grade Bigel.Biomacromolecules. 2025 May 12;26(5):2800-2810. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.4c00959. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Biomacromolecules. 2025. PMID: 39703056
-
Bigels; A Charismatic Drug Delivery Formulation.Drug Metab Bioanal Lett. 2023 May 1. doi: 10.2174/2949681016666230501172824. Online ahead of print. Drug Metab Bioanal Lett. 2023. PMID: 37125832
-
Novel bigel based on nanocellulose hydrogel and monoglyceride oleogel: Preparation, characteristics and application as fat substitute.Food Res Int. 2024 Dec;198:115397. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.115397. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39643352
-
Novel approaches in food grade bigels properties and applications: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Dec;283(Pt 3):137424. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.137424. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39537066 Review.
-
Food-Grade Bigel Systems: Formulation, Characterization, and Applications for Novel Food Product Development.Gels. 2024 Nov 3;10(11):712. doi: 10.3390/gels10110712. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39590068 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characteristics and Functional Properties of Bioactive Oleogels: A Current Review.Gels. 2025 Jan 16;11(1):69. doi: 10.3390/gels11010069. Gels. 2025. PMID: 39852041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D Printed Bigel: A Novel Delivery System for Cannabidiol-Rich Hemp Extract.Gels. 2024 Nov 26;10(12):770. doi: 10.3390/gels10120770. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39727528 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing Gel Systems with Natural Extracts: Antioxidant, Antimicrobial Applications, and Sustainable Innovations.Gels. 2025 Feb 8;11(2):125. doi: 10.3390/gels11020125. Gels. 2025. PMID: 39996668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Waxes as Gelators in Edible Structured Oil Systems: A Review.Gels. 2025 Aug 18;11(8):656. doi: 10.3390/gels11080656. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40868786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tuning Nanostructure of Gels: From Structural and Functional Controls to Food Applications.Gels. 2025 Aug 8;11(8):620. doi: 10.3390/gels11080620. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40868751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- FMI US Grocery Shopper Trends: A Look at Today’s Grocery Shopper. Food Marketing Institute; Washington, DC, USA: 2019.
-
- WHO Countdown to 2023: WHO Report on Global Trans Fat Elimination 2021. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2021.
-
- McClements D.J. Designing Biopolymer Microgels to Encapsulate, Protect and Deliver Bioactive Components: Physicochemical Aspects. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;240:31–59. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

