Recombinant Soybean Lipoxygenase 2 (GmLOX2) Acts Primarily as a ω6(S)-Lipoxygenase
- PMID: 37623215
- PMCID: PMC10452975
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb45080396
Recombinant Soybean Lipoxygenase 2 (GmLOX2) Acts Primarily as a ω6(S)-Lipoxygenase
Abstract
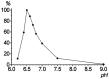
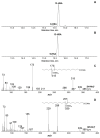
The lipoxygenase (LOX) cascade is a source of bioactive oxylipins that play a regulatory role in plants, animals, and fungi. Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) LOXs are the classical models for LOX research. Progress in genomics has uncovered a large diversity of GmLOX isoenzymes. Most of them await biochemical investigations. The catalytic properties of recombinant soybean LOX2 (GmLOX2) are described in the present work. The GmLOX2 gene has been cloned before, but only for nucleotide sequencing, while the recombinant protein was not prepared and studied. In the present work, the recombinant GmLOX2 behavior towards linoleic, α-linolenic, eicosatetraenoic (20:4), eicosapentaenoic (20:5), and hexadecatrienoic (16:3) acids was examined. Linoleic acid was a preferred substrate. Oxidation of linoleic acid afforded 94% optically pure (13S)-hydroperoxide and 6% racemic 9-hydroperoxide. GmLOX2 was less active on other substrates but possessed an even higher degree of regio- and stereospecificity. For example, it converted α-linolenic acid into (13S)-hydroperoxide at about 98% yield. GmLOX2 showed similar specificity towards other substrates, producing (15S)-hydroperoxides (with 20:4 and 20:5) or (11S)-hydroperoxide (with 16:3). Thus, the obtained data demonstrate that soybean GmLOX2 is a specific (13S)-LOX. Overall, the catalytic properties of GmLOX2 are quite similar to those of GmLOX1, but pH is optimum.
Keywords: fatty acid oxidation; lipoxygenase-2; regio- and stereospecificity; soybean; substrate specificity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and analysis of LOX genes in soybean cultivar "Zhonghuang 13".Front Genet. 2022 Oct 7;13:1020554. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1020554. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36276975 Free PMC article.
-
On the relationships of substrate orientation, hydrogen abstraction, and product stereochemistry in single and double dioxygenations by soybean lipoxygenase-1 and its Ala542Gly mutant.J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 18;280(46):38756-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M504870200. Epub 2005 Sep 12. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16157595 Free PMC article.
-
Catalytic characterization of heterodimeric linoleate 13S-lipoxygenase from black soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.).Enzyme Microb Technol. 2020 Sep;139:109595. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2020.109595. Epub 2020 May 20. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2020. PMID: 32732043
-
The structural basis for specificity in lipoxygenase catalysis.Protein Sci. 2015 Mar;24(3):298-309. doi: 10.1002/pro.2626. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Protein Sci. 2015. PMID: 25524168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological significance of essential fatty acids/prostanoids/lipoxygenase-derived monohydroxy fatty acids in the skin.Arch Pharm Res. 2002 Dec;25(6):747-58. doi: 10.1007/BF02976988. Arch Pharm Res. 2002. PMID: 12510822 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the lipoxygenase gene family in sesame reveals regulatory networks in response to abiotic stress.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Feb 27;52(1):266. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10371-z. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40014160
-
Quercetin: A Potential Polydynamic Drug.Molecules. 2023 Dec 17;28(24):8141. doi: 10.3390/molecules28248141. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138630 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vliegenthart J.F.G., Veldink G.A. Lipoxygenases, Nonheme Iron-Containing Enzymes. Adv. Inorg. Biochem. 1984;6:139–161. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

