Artificial Intelligence-Based Methods for Precision Cardiovascular Medicine
- PMID: 37623518
- PMCID: PMC10455092
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13081268
Artificial Intelligence-Based Methods for Precision Cardiovascular Medicine
Abstract
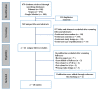
Precision medicine has the potential to revolutionize the way cardiovascular diseases are diagnosed, predicted, and treated by tailoring treatment strategies to the individual characteristics of each patient. Artificial intelligence (AI) has recently emerged as a promising tool for improving the accuracy and efficiency of precision cardiovascular medicine. In this scoping review, we aimed to identify and summarize the current state of the literature on the use of AI in precision cardiovascular medicine. A comprehensive search of electronic databases, including Scopes, Google Scholar, and PubMed, was conducted to identify relevant studies. After applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, a total of 28 studies were included in the review. We found that AI is being increasingly applied in various areas of cardiovascular medicine, including the diagnosis, prognosis of cardiovascular diseases, risk prediction and stratification, and treatment planning. As a result, most of these studies focused on prediction (50%), followed by diagnosis (21%), phenotyping (14%), and risk stratification (14%). A variety of machine learning models were utilized in these studies, with logistic regression being the most used (36%), followed by random forest (32%), support vector machine (25%), and deep learning models such as neural networks (18%). Other models, such as hierarchical clustering (11%), Cox regression (11%), and natural language processing (4%), were also utilized. The data sources used in these studies included electronic health records (79%), imaging data (43%), and omics data (4%). We found that AI is being increasingly applied in various areas of cardiovascular medicine, including the diagnosis, prognosis of cardiovascular diseases, risk prediction and stratification, and treatment planning. The results of the review showed that AI has the potential to improve the performance of cardiovascular disease diagnosis and prognosis, as well as to identify individuals at high risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. However, further research is needed to fully evaluate the clinical utility and effectiveness of AI-based approaches in precision cardiovascular medicine. Overall, our review provided a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge in the field of AI-based methods for precision cardiovascular medicine and offered new insights for researchers interested in this research area.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; cardiovascular diseases; machine learning; precision medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artificial Intelligence in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current Status and Future Perspectives: A State-of-the-Art Review.Rheumatol Ther. 2022 Oct;9(5):1249-1304. doi: 10.1007/s40744-022-00475-4. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Rheumatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35849321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence for cardiovascular disease risk assessment in personalised framework: a scoping review.EClinicalMedicine. 2024 May 27;73:102660. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102660. eCollection 2024 Jul. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 38846068 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence-based methods for fusion of electronic health records and imaging data.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 26;12(1):17981. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22514-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36289266 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Predicting Facial Changes Post-Orthognathic Surgery: A Comprehensive Scoping Review.J Clin Exp Dent. 2024 May 1;16(5):e624-e633. doi: 10.4317/jced.61500. eCollection 2024 May. J Clin Exp Dent. 2024. PMID: 38988747 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence: improving the efficiency of cardiovascular imaging.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2020 Jun;17(6):565-577. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2020.1777855. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2020. PMID: 32510252 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Big data in breast cancer: Towards precision treatment.Digit Health. 2024 Nov 3;10:20552076241293695. doi: 10.1177/20552076241293695. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39502482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic medicine and personalized treatment: a narrative review.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 Feb 13;87(3):1406-1414. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002965. eCollection 2025 Mar. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40213198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in the Prediction, Diagnosis, and Management of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2025 Mar 28;17(3):e81332. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81332. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40291312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Digital Health Solutions for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: Systematic Review.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jan 23;27:e64981. doi: 10.2196/64981. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39847411 Free PMC article.
-
Transformative Potential of AI in Healthcare: Definitions, Applications, and Navigating the Ethical Landscape and Public Perspectives.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Jan 5;12(2):125. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12020125. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38255014 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) [(accessed on 25 December 2022)]. Available online: https://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10025942218/
-
- Roth G.A., Mensah G.A., Johnson C.O., Addolorato G., Ammirati E., Baddour L.M., Barengo N.C., Beaton A.Z., Benjamin E.J., Benziger C.P., et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;76:2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dunbar S.B., Khavjou O.A., Bakas T., Hunt G., Kirch R.A., Leib A.R., Morrison R.S., Poehler D.C., Roger V.L., Whitsel L.P. Projected Costs of Informal Caregiving for Cardiovascular Disease: 2015 to 2035: A Policy Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137:e558–e577. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000570. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mesko B. The role of artificial intelligence in precision medicine. Expert Rev. Precis. Med. Drug Dev. 2017;2:239–241. doi: 10.1080/23808993.2017.1380516. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials