Investigating the Structure of the French WISC-V (WISC-VFR) for Five Age Groups Using Psychometric Network Modeling
- PMID: 37623543
- PMCID: PMC10455472
- DOI: 10.3390/jintelligence11080160
Investigating the Structure of the French WISC-V (WISC-VFR) for Five Age Groups Using Psychometric Network Modeling
Abstract
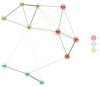
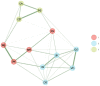
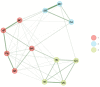
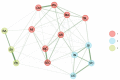
Since the seminal work of Spearman, exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis represents the standard method of examining the dimensionality of psychological instruments. Recently, within the network psychometrics approach, a new procedure was proposed to estimate the dimensionality of psychological instruments: exploratory graph analysis (EGA). This study investigated the structure of the French Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Fifth Edition (WISC-VFR) with five standardization sample age groups (6-7, 8-9, 10-11, 12-13, and 14-16 years) using EGA. The primary research questions include (a) how many WISC-VFR dimensions are identified in each age subgroup? (b) how are subtest scores associated within the dimensions? Because the number and the content of the dimensions identified by EGA could vary with samples, the secondary research questions include (c) is there evidence of reproducibility and generalizability of the dimensions identified by EGA? We used another procedure called bootstrap exploratory graph analysis (bootEGA). EGA and bootEGA suggested only three dimensions, which are consistent with processing speed, verbal comprehension, and the "old" perceptual reasoning factor. Results did not support the distinction between visual-spatial and fluid reasoning dimensions. EGA and bootEGA represent new tools to assess the construct validity of psychological instruments, such as the WISC-VFR.
Keywords: WISC–VFR; age; bootEGA; construct validity; dimensionality; exploratory graph analysis (EGA); intelligence; psychometric network analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association, and National Council on Measurement in Education . Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing. American Educational Research Association; Washington, DC: 2014.
-
- Beaujean A. Alexander. Adopting a new test edition: Psychometric and practical considerations. Research and Practice in the Schools. 2015;3:51–57.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources