Use of Dichlorodimethylsilane to Produce Polydimethylsiloxane as a Substitute for Vitreous Humour: Characteristics and In Vitro Toxicity
- PMID: 37623669
- PMCID: PMC10455291
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb14080425
Use of Dichlorodimethylsilane to Produce Polydimethylsiloxane as a Substitute for Vitreous Humour: Characteristics and In Vitro Toxicity
Abstract
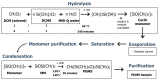
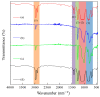
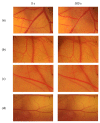
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is a substitute for vitreous humour in vitreoretinal surgery and is usually produced from octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane (D4). In Indonesia, both commercial PDMS and D4 are limited and expensive. Dichlorodimethylsilane (DCMS) can be an alternative to produce PDMS. DCMS is cheaper and easier to obtain than D4. However, more extra effort is needed in order to produce PDMS from DCMS. Therefore, this study aimed to produce PDMS from DCMS by varying the ratio of DCMS precursor to dichloromethane (DCM) solvent at ratios of 1:1 and 1:4 through the hydrolysis-condensation method under neutral conditions. The PDMS produced had medium- (2.06 Pa·s) and high viscosity (3.59 Pa·s), with densities ranging from 0.96 to 0.99 g/mL. The refractive index was 1.4034-1.4036 and surface tension was 21 × 10-3 N/m, while they were able to transmit ~100% visible light, which were similar values to the commercial PDMS characteristics. PDMS samples were characterized using IR and NMR spectroscopy, which confirmed they were of PDMS type. The most optimum DCMS:DCM ratio was 1:1 due to the medium-viscosity PDMS type that could be produced. The in vitro HET-CAM toxicity test showed that samples were non-irritant, similar to PDMS produced from D4. PDMS from DCMS was non-toxic and ready to be used as a vitreous humuor substitution.
Keywords: DCM; DCMS; PDMS; high viscosity; hydrolysis–condensation; in vitro toxicity; medium viscosity; optimization; ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Physical Characterization and In Vitro Toxicity Test of PDMS Synthesized from Low-Grade D4 Monomer as a Vitreous Substitute in the Human Eyes.J Funct Biomater. 2022 Jan 2;13(1):3. doi: 10.3390/jfb13010003. J Funct Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35076527 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale synthesis of polydimethylsiloxane as vitreous replacement applications.Des Monomers Polym. 2025 Jan 8;28(1):1-6. doi: 10.1080/15685551.2024.2449442. eCollection 2025. Des Monomers Polym. 2025. PMID: 39802405 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Low-Temperature Chemical Vapor Deposition of Hydrothermal Delignified Wood for Hydrophobic Property.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Aug 6;12(8):1757. doi: 10.3390/polym12081757. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32781550 Free PMC article.
-
Silicone Surface Fundamentals.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2021 Mar;42(5):e2000360. doi: 10.1002/marc.202000360. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2021. PMID: 32935908 Review.
-
[Environmental behavior and ecological effect of polydimethylsiloxane: a review].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2012 Aug;23(8):2319-24. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 23189715 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Tailoring polymethylhydrosiloxane as candidate material for vitreous humour substitution: physical properties and in vitro toxicity.BMC Chem. 2025 Jul 11;19(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s13065-025-01548-5. BMC Chem. 2025. PMID: 40646567 Free PMC article.
-
Photoacoustic method for measuring the elasticity of polydimethylsiloxane at various mixing ratios.Heliyon. 2024 May 22;10(11):e31726. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31726. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38841497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baino F. The Use of Polymers in the Treatment of Retinal Detachment: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Polymers. 2010;2:286–322. doi: 10.3390/polym2030286. - DOI
-
- Khurana A.K. Comprehensive Ophtalmology. 6rd, ed. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.; New Delhi, India: 2015.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

