Secondary Metabolites, Biological Activities, and Industrial and Biotechnological Importance of Aspergillus sydowii
- PMID: 37623723
- PMCID: PMC10455642
- DOI: 10.3390/md21080441
Secondary Metabolites, Biological Activities, and Industrial and Biotechnological Importance of Aspergillus sydowii
Abstract
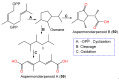
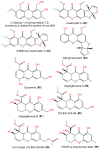
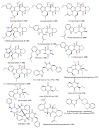
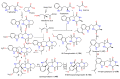
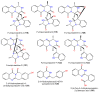
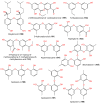
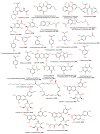
Marine-derived fungi are renowned as a source of astonishingly significant and synthetically appealing metabolites that are proven as new lead chemicals for chemical, pharmaceutical, and agricultural fields. Aspergillus sydowii is a saprotrophic, ubiquitous, and halophilic fungus that is commonly found in different marine ecosystems. This fungus can cause aspergillosis in sea fan corals leading to sea fan mortality with subsequent changes in coral community structure. Interestingly, A. sydowi is a prolific source of distinct and structurally varied metabolites such as alkaloids, xanthones, terpenes, anthraquinones, sterols, diphenyl ethers, pyrones, cyclopentenones, and polyketides with a range of bioactivities. A. sydowii has capacity to produce various enzymes with marked industrial and biotechnological potential, including α-amylases, lipases, xylanases, cellulases, keratinases, and tannases. Also, this fungus has the capacity for bioremediation as well as the biocatalysis of various chemical reactions. The current work aimed at focusing on the bright side of this fungus. In this review, published studies on isolated metabolites from A. sydowii, including their structures, biological functions, and biosynthesis, as well as the biotechnological and industrial significance of this fungus, were highlighted. More than 245 compounds were described in the current review with 134 references published within the period from 1975 to June 2023.
Keywords: Aspergillus sydowii; bioremediation; biotechnology; drug discovery; enzymes; fungi; life on land; marine natural products; metabolites; renewable resources.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures













References
-
- Ibrahim S.R., Mohamed G.A., Al Haidari R.A., El-Kholy A.A., Zayed M.F., Khayat M.T. Biologically Active Fungal Depsidones: Chemistry, Biosynthesis, Structural Characterization, and Bioactivities. Fitoterapia. 2018;129:317–365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

