Lobosteroids A-F: Six New Highly Oxidized Steroids from the Chinese Soft Coral Lobophytum sp
- PMID: 37623738
- PMCID: PMC10456462
- DOI: 10.3390/md21080457
Lobosteroids A-F: Six New Highly Oxidized Steroids from the Chinese Soft Coral Lobophytum sp
Abstract
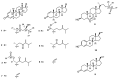
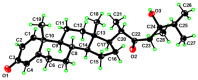
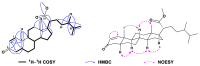
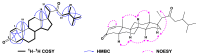
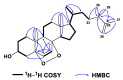
To explore the steroidal constituents of the soft coral Lobophytum sp. at the coast of Xuwen County, Guangdong Province, China, a chemical investigation of the above-mentioned soft coral was carried out. After repeated column chromatography over silica gel, Sephadex LH-20, and reversed-phase HPLC, six new steroids, namely lobosteroids A-F (1-6), along with four known compounds 7-10, were obtained. Their structures were determined by extensive spectroscopic analysis and comparison with the spectral data reported in the literature. Among them, the absolute configuration of 1 was determined by X-ray diffraction analysis using Cu Kα radiation. These steroids were characterized by either the presence of an α,β-α',β'-unsaturated carbonyl, or an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl moiety in ring A, or the existence of a 5α,8α-epidioxy system in ring B, as well as diverse oxidation of side chains. The antibacterial bioassays showed that all isolated steroids exhibited significant inhibitory activities against the fish pathogenic bacteria Streptococcus parauberis FP KSP28, Phoyobacterium damselae FP2244, and Streptococcus parauberis SPOF3K, with IC90 values ranging from 0.1 to 11.0 µM. Meanwhile, compounds 2 and 6-10 displayed potent inhibitory effects against the vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium bacterium G7 with IC90 values ranging from 4.4 to 18.3 µM. Therefore, ten highly oxidized steroids with strong antibacterial activities were isolated from the Chinese soft coral Lobophytum sp., which could be developed as new chemotypes of antibacterial drug leads.
Keywords: Lobophytum sp.; antibacterial activity; soft coral; steroids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
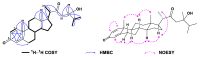
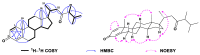
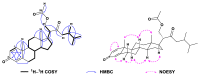
Similar articles
-
Bioactive Steroids with Structural Diversity from the South China Sea Soft Coral Lobophytum sp. and Sponge Xestospongia sp.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jan 13;23(1):36. doi: 10.3390/md23010036. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39852538 Free PMC article.
-
Nine New Antibacterial Diterpenes and Steroids from the South China Sea Soft Coral Lobophytum catalai Tixier-Durivault.Mar Drugs. 2024 Jan 20;22(1):50. doi: 10.3390/md22010050. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38276652 Free PMC article.
-
Four uncommon cycloamphilectane-type diterpenoids with antibacterial activity from the South China Sea soft coral Sinularia brassica.Phytochemistry. 2024 Mar;219:113960. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2023.113960. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Phytochemistry. 2024. PMID: 38159620
-
Oxygenated Cembrane Diterpenes from the South China Sea Soft Coral Sinularia tumulosa.Chem Biodivers. 2023 Jul;20(7):e202300589. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202300589. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Chem Biodivers. 2023. PMID: 37254228
-
Sinulasterols D-G, four new antibacterial steroids from the South China sea soft coral Sinularia depressa.Steroids. 2023 Apr;192:109182. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2023.109182. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Steroids. 2023. PMID: 36642107
Cited by
-
Metabolic Profiling, Antiviral Activity and the Microbiome of Some Mauritian Soft Corals.Mar Drugs. 2023 Oct 31;21(11):574. doi: 10.3390/md21110574. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37999398 Free PMC article.
-
Sterebellosides A-F, Six New Diterpene Glycosides from the Soft Coral Stereonephthya bellissima.Mar Drugs. 2025 Mar 11;23(3):121. doi: 10.3390/md23030121. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40137307 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Steroids with Structural Diversity from the South China Sea Soft Coral Lobophytum sp. and Sponge Xestospongia sp.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jan 13;23(1):36. doi: 10.3390/md23010036. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39852538 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

