Improvement of MBBR-MBR Performance by the Addition of Commercial and 3D-Printed Biocarriers
- PMID: 37623751
- PMCID: PMC10456846
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes13080690
Improvement of MBBR-MBR Performance by the Addition of Commercial and 3D-Printed Biocarriers
Abstract
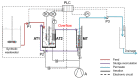
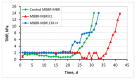
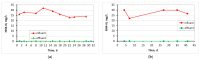
Moving bed biofilm reactor combined with membrane bioreactor (MBBR-MBR) constitute a highly effective wastewater treatment technology. The aim of this research work was to study the effect of commercial K1 biocarriers (MBBR-MBR K1 unit) and 3D-printed biocarriers fabricated from 13X and Halloysite (MBBR-MBR 13X-H unit), on the efficiency and the fouling rate of an MBBR-MBR unit during wastewater treatment. Various physicochemical parameters and trans-membrane pressure were measured. It was observed that in the MBBR-MBR K1 unit, membrane filtration improved reaching total membrane fouling at 43d, while in the MBBR-MBR 13X-H and in the control MBBR-MBR total fouling took place at about 32d. This is attributed to the large production of soluble microbial products (SMP) in the MBBR-MBR 13X-H, which resulted from a large amount of biofilm created in the 13X-H biocarriers. An optimal biodegradation of the organic load was concluded, and nitrification and denitrification processes were improved at the MBBR-MBR K1 and MBBR-MBR 13X-H units. The dry mass produced on the 13X-H biocarriers ranged at 4980-5711 mg, three orders of magnitude larger than that produced on the K1, which ranged at 2.9-4.6 mg. Finally, it was observed that mostly extracellular polymeric substances were produced in the biofilm of K1 biocarriers while in 13X-H mostly SMP.
Keywords: 13X-halloysite biocarriers; 3D-printed biocarriers; EPS; Kaldnes K1 biocarriers; MBBR-MBR; SMP; biofilm; colloidal particles; membrane fouling; wastewater treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



















References
-
- Saidulu D., Majumder A., Gupta A.K. A systematic review of moving bed biofilm reactor, membrane bioreactor, and moving bed membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment: Comparison of research trends, removal mechanisms, and performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021;9:106112. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.106112. - DOI
-
- Leyva-Díaz J.C., Monteoliva-García A., Martín-Pascual J., Munio M.M., García-Mesa J.J., Poyatos J.M. Moving bed biofilm reactor as an alternative wastewater treatment process for nutrient removal and recovery in the circular economy model. Bioresour. Technol. 2020;299:122631. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122631. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu J., Sun F., Zhang P., Zhou Y. Integrated powdered activated carbon and quorum quenching strategy for biofouling control in industrial wastewater membrane bioreactor. J. Clean. Prod. 2021;279:123551. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123551. - DOI
-
- Kawan J.A., Abu Hasan H., Suja F., Jaafar O., Abd-Rahman R. A review on sewage treatment and polishing using moving bed bioreactor (MBBR) J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2016;11:1098–1120. doi: 10.13140/RG.2.2.19104.17922. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

