Biologically Relevant Murine Models of Chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa Respiratory Infection
- PMID: 37624013
- PMCID: PMC10458525
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12081053
Biologically Relevant Murine Models of Chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa Respiratory Infection
Abstract
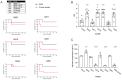
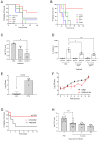
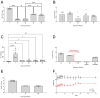
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) is an opportunistic pathogen and the leading cause of infection in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF). The ability of P. aeruginosa to evade host responses and develop into chronic infection causes significant morbidity and mortality. Several mouse models have been developed to study chronic respiratory infections induced by P. aeruginosa, with the bead agar model being the most widely used. However, this model has several limitations, including the requirement for surgical procedures and high mortality rates. Herein, we describe novel and adapted biologically relevant models of chronic lung infection caused by P. aeruginosa. Three methods are described: a clinical isolate infection model, utilising isolates obtained from patients with CF; an incomplete antibiotic clearance model, leading to bacterial bounce-back; and the establishment of chronic infection; and an adapted water bottle chronic infection model. These models circumvent the requirement for a surgical procedure and, importantly, can be induced with clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa and in wild-type mice. We also demonstrate successful induction of chronic infection in the transgenic βENaC murine model of CF. We envisage that the models described will facilitate the investigations of host and microbial factors, and the efficacy of novel antimicrobials, during chronic P. aeruginosa respiratory infections.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; S. aureus; chronic infection; in vivo; murine model; respiratory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Scnn1b-Transgenic BALB/c Mice as a Model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections of the Cystic Fibrosis Lung.Infect Immun. 2020 Aug 19;88(9):e00237-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00237-20. Print 2020 Aug 19. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32631918 Free PMC article.
-
The Small RNA ErsA Plays a Role in the Regulatory Network of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pathogenicity in Airway Infections.mSphere. 2020 Oct 14;5(5):e00909-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00909-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 33055260 Free PMC article.
-
Genotypic and Phenotypic Diversity of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Cystic Fibrosis Patient Lung Infections and Their Interactions with Pseudomonas aeruginosa.mBio. 2020 Jun 23;11(3):e00735-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00735-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32576671 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of chronic lung infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa: models for the study of cystic fibrosis.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2000 Nov;30(5):413-24. doi: 10.1002/1099-0496(200011)30:5<413::aid-ppul8>3.0.co;2-9. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2000. PMID: 11064433 Review.
-
Potential of preventing Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections in cystic fibrosis patients: experimental studies in animals.APMIS Suppl. 1996;63:5-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.1996.tb05581.x. APMIS Suppl. 1996. PMID: 8944052 Review.
Cited by
-
A chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa mouse lung infection modeling the mucus obstruction, lung function, and inflammation of human cystic fibrosis.Infect Immun. 2025 Jul 8;93(7):e0023025. doi: 10.1128/iai.00230-25. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Infect Immun. 2025. PMID: 40512037 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of Agar Bead Embedded Mycobacterium abscessus to Inoculate Immunocompetent Mice Intratracheally.J Vis Exp. 2025 Apr 25;(218):10.3791/67602. doi: 10.3791/67602. J Vis Exp. 2025. PMID: 40354234 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical murine models for the testing of antimicrobials against Mycobacterium abscessus pulmonary infections: Current practices and recommendations.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2024 Jul;147:102503. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2024.102503. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2024. PMID: 38729070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa mouse lung infection modeling the pathophysiology and inflammation of human cystic fibrosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 7:2024.10.07.617039. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.07.617039. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Infect Immun. 2025 Jul 8;93(7):e0023025. doi: 10.1128/iai.00230-25. PMID: 39416002 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Osbourn M., Rodgers A.M., Dubois A.V., Small D.M., Humphries F., Delagic N., Moynagh P.N., Weldon S., Taggart C.C., Ingram R.J. Secretory Leucoprotease Inhibitor (SLPI) Promotes Survival during Acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection by Suppression of Inflammation Rather Than Microbial Killing. Biomolecules. 2022;12:1728. doi: 10.3390/biom12121728. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

