Anti- Toxoplasma gondii Effects of Lipopeptide Derivatives of Lycosin-I
- PMID: 37624234
- PMCID: PMC10467082
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins15080477
Anti- Toxoplasma gondii Effects of Lipopeptide Derivatives of Lycosin-I
Abstract
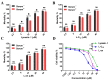
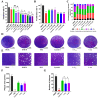
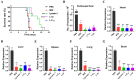
Toxoplasmosis, caused by Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii), is a serious zoonotic parasitic disease. We previously found that Lycosin-I exhibited anti-T. gondii activity, but its serum stability was not good enough. In this study, we aimed to improve the stability and activity of Lycosin-I through fatty acid chain modification, so as to find a better anti-T. gondii drug candidate. The α/ε-amino residues of different lysine residues of Lycosin-I were covalently coupled with lauric acid to obtain eight lipopeptides, namely L-C12, L-C12-1, L-C12-2, L-C12-3, L-C12-4, L-C12-5, L-C12-6, and L-C12-7. Among these eight lipopeptides, L-C12 showed the best activity against T. gondii in vitro in a trypan blue assay. We then conjugated a shorter length fatty chain, aminocaproic acid, at the same modification site of L-C12, namely L-an. The anti-T. gondii effects of Lycosin-I, L-C12 and L-an were evaluated via an invasion assay, proliferation assay and plaque assay in vitro. A mouse model acutely infected with T. gondii tachyzoites was established to evaluate their efficacy in vivo. The serum stability of L-C12 and L-an was improved, and they showed comparable or even better activity than Lycosin-I did in inhibiting the invasion and proliferation of tachyzoites. L-an effectively prolonged the survival time of mice acutely infected with T. gondii. These results suggest that appropriate fatty acid chain modification can improve serum stability and enhance anti-T. gondii effect of Lycosin-I. The lipopeptide derivatives of Lycosin-I have potential as a novel anti-T. gondii drug candidate.
Keywords: Lycosin-I; Toxoplasma gondii; fatty acid chain modification; lipopeptide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anti-parasitic effect on Toxoplasma gondii induced by a spider peptide lycosin-I.Exp Parasitol. 2019 Mar;198:17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2019.01.009. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Exp Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 30682337
-
Position Effect of Fatty Acid Modification on the Cytotoxicity and Antimetastasis Potential of the Cytotoxic Peptide Lycosin-I.J Med Chem. 2019 Dec 26;62(24):11108-11118. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01126. Epub 2019 Dec 4. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31735030
-
The Roles of Fatty-Acid Modification in the Activity of the Anticancer Peptide R-Lycosin-I.Mol Pharm. 2018 Oct 1;15(10):4612-4620. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00605. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30183307
-
Glucose-Lipopeptide Conjugates Reveal the Role of Glucose Modification Position in Complexation and the Potential of Malignant Melanoma Therapy.J Med Chem. 2021 Aug 12;64(15):11483-11495. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00805. Epub 2021 Jul 20. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34282902
-
Lipid metabolism: the potential targets for toxoplasmosis treatment.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Mar 6;17(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06213-9. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38448975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LC-AMP-I1, a novel venom-derived antimicrobial peptide from the wolf spider Lycosa coelestis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025 Jan 31;69(1):e0042424. doi: 10.1128/aac.00424-24. Epub 2024 Dec 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025. PMID: 39620694 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects and Mechanism of ATM Kinase Inhibitors in Toxoplasma gondii.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 25;25(13):6947. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136947. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000057 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

