Purification and Activity of the Second Recombinant Enzyme for Biodegrading Linearized Microcystins by Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05
- PMID: 37624251
- PMCID: PMC10467064
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins15080494
Purification and Activity of the Second Recombinant Enzyme for Biodegrading Linearized Microcystins by Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05
Abstract
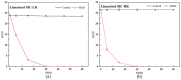
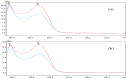
Hepatotoxic microcystins (MCs) are produced and released by the harmful bloom-forming cyanobacteria, which severely threaten drinking water safety and human health due to their high toxicity, widespread distribution, and structural stability. The linearized microcystinase (MlrB) further hydrolyses the poisonous linearized MCs produced by the microcystinase-catalysed MCs to form tetrapeptides. Here, the purification and activity of MlrB were investigated. The results showed that the linearized products generated by 12.5 mg/L MC-LR and MC-RR were removed by purified recombinant MlrB at a protein concentration of 1 mg/L within 30 min. The high catalytic activity of MlrB can be obtained via heterologous expression and affinity purification, which lays the foundation for further studies on the properties and mechanism of MCs biodegradation enzymes.
Keywords: activity; biodegradation; linearized microcystinase; microcystins; purification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enzymatic mechanism of MlrB for catalyzing linearized microcystins by Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 22;15:1389235. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1389235. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38711965 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and Mechanism of Microcystinase MlrC for Catalyzing Linearized Cyanobacterial Hepatotoxins Using Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Aug 31;14(9):602. doi: 10.3390/toxins14090602. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36136540 Free PMC article.
-
The detoxification activities and mechanisms of microcystinase towards MC-LR.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022 May 1;236:113436. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113436. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022. PMID: 35367885
-
[Advances in the pathway and molecular mechanism for the biodegradation of microcystins].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2014 Mar;35(3):1205-14. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2014. PMID: 24881418 Review. Chinese.
-
A Mini Review on Microcystins and Bacterial Degradation.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Apr 21;12(4):268. doi: 10.3390/toxins12040268. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32326338 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Morchella Effectively Removes Microcystins Produced by Microcystis aeruginosa.Microbes Environ. 2024;39(2):ME23101. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME23101. Microbes Environ. 2024. PMID: 38763742 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic mechanism of MlrB for catalyzing linearized microcystins by Sphingopyxis sp. USTB-05.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 22;15:1389235. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1389235. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38711965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mariani M.A., Padedda B.M., Kaštovský J., Buscarinu P., Sechi N., Virdis T., Lugliè A. Effects of trophic status on microcystin production and the dominance of cyanobacteria in the phytoplankton assemblage of Mediterranean reservoirs. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:17964. doi: 10.1038/srep17964. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heresztyn T., Nicholson B.C. Nodularin concentrations in Lakes Alexandrina and Albert, South Australia, during a bloom of the cyanobacterium (bluegreen alga) Nodularia spumigena and degradation of the toxin. Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual. 1997;12:273–282. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2256(1997)12:4<273::AID-TOX1>3.0.CO;2-5. - DOI
-
- Codd G., Bell S., Kaya K., Ward C., Beattie K., Metcalf J. Cyanobacterial toxins, exposure routes and human health. Eur. J. Phycol. 1999;34:405–415. doi: 10.1080/09670269910001736462. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

