A Multi-Layer-Controlled Strategy for Cloning and Expression of Toxin Genes in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 37624265
- PMCID: PMC10467106
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins15080508
A Multi-Layer-Controlled Strategy for Cloning and Expression of Toxin Genes in Escherichia coli
Abstract
Molecular cloning and controlled expression remain challenging when the target gene encodes a protein that is toxic to the host. We developed a set of multi-layer control systems to enable cloning of genes encoding proteins known to be highly toxic in Escherichia coli and other bacteria. The different multi-layer control systems combine a promoter-operator system on a transcriptional level with a riboswitch for translational control. Additionally, replicational control is ensured by using a strain that reduces the plasmid copy number. The use of weaker promoters (such as PBAD or PfdeA) in combination with the effective theophylline riboswitch is essential for cloning genes that encode notoriously toxic proteins that directly target translation and transcription. Controlled overexpression is possible, allowing the system to be used for evaluating in vivo effects of the toxin. Systems with a stronger promoter can be used for successful overexpression and purification of the desired protein but are limited to toxins that are more moderate and do not interfere with their own production.
Keywords: cloning; replicational control; riboswitch; toxins; transcriptional control; translational control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
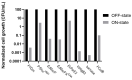
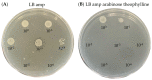
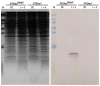
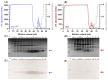
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

