Effect of Penthorum Chinense Pursh Compound on AFB1-Induced Immune Imbalance via JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in Spleen of Broiler Chicken
- PMID: 37624308
- PMCID: PMC10459701
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci10080521
Effect of Penthorum Chinense Pursh Compound on AFB1-Induced Immune Imbalance via JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway in Spleen of Broiler Chicken
Abstract
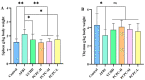
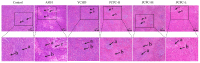
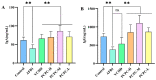
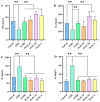
Aflatoxin B1(AFB1) is the main secondary metabolite produced by Aspergillus flavus, which is highly toxic, carcinogenic, mutagenic and teratogenic. It can induce immune imbalance in animals or humans. Penthorum chinense Pursh (PCP) is a traditional herbal plant that has been used as a hepatoprotective drug with a long history in China. Based on the theory of traditional Chinese Medicine, we prepared Penthorum chinense Pursh Compound (PCPC) by combining four herbal medicines: 5 g Penthorum chinense Pursh, 5 g Radix bupleuri, 1 g Artemisia capillaris Thunb and 1 g Radix glycyrrhizae. The role of the Penthorum chinense Pursh Compound (PCPC) in preventing AFB1-induced immune imbalance in broiler chickens was studied. A total of 180 broiler chickens were equally distributed in six groups: controls, AFB1, YCHD and high-, medium- and low-dose PCPC treatment groups. After 28 days, broilers were anesthetized, and serum spleen and thymus samples were collected for analysis. Results show that AFB1 significantly increased and decreased the relative organ weight of the spleen and thymus, respectively. Pathological section of hematoxylin/eosin (H&E) stained spleen sections showed that AFB1 resulted in splenic tissue damage. Both the serum levels of Immunoglobulin A (IgA) and Immunoglobulin G (IgG) were suppressed in the AFB1 group. IL-6 was elevated in the AFB1 group. The balance between pro-inflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ and IL-2) and anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-4) was disturbed by AFB1. The apoptosis-related protein and JAK/STAT pathway-related gene expression indicated that AFB1-induced apoptosis via JAK/STAT pathway. PCPC has proven its immunoprotective effects by preventing AFB1-induced immune imbalance. PCPC can be applied as a novel immune-modulating medicine in broiler chickens. It can be applied as a novel immune modulator in veterinary clinical practice.
Keywords: AFB1; Broiler chicken; JAK/STAT signaling pathway; Penthorum chinense Pursh Compound; apoptosis; immune imbalance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Penthorum chinense Pursh Compound Ameliorates AFB1-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis via Modulation of Mitochondrial Pathways in Broiler Chicken Kidneys.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Oct 8;8:750937. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.750937. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34692815 Free PMC article.
-
Penthorum chinense Pursh compound flavonoids supplementation alleviates Aflatoxin B1-induced liver injury via modulation of intestinal barrier and gut microbiota in broiler.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023 Apr 15;255:114805. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114805. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023. PMID: 36958264
-
Penthorum Chinense Pursh Extract Alleviates Aflatoxin B1-Induced Liver Injury and Oxidative Stress Through Mitochondrial Pathways in Broilers.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Feb 2;9:822259. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.822259. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35187148 Free PMC article.
-
An Updated Review on Efficiency of Penthorum chinense Pursh in Traditional Uses, Toxicology, and Clinical Trials.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Feb 18;2023:4254051. doi: 10.1155/2023/4254051. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36852294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of Penthorum chinense Pursh for hepatoprotection: Traditional use, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and clinical trials.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Apr 6;251:112569. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112569. Epub 2020 Jan 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31935496 Review.
Cited by
-
AFB1 Toxicity in Human Food and Animal Feed Consumption: A Review of Experimental Treatments and Preventive Measures.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 13;25(10):5305. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105305. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Dietary Baicalin on Aflatoxin B1-Induced Growth Performance and Liver Health in Ducklings.Animals (Basel). 2025 Aug 8;15(16):2325. doi: 10.3390/ani15162325. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40867655 Free PMC article.
-
Danshen Polysaccharides Alleviate Aflatoxin B1-Induced Liver Damage and Immune Disorders by Inhibiting the ROS-Mediated Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Aug 13;14(8):991. doi: 10.3390/antiox14080991. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40867887 Free PMC article.
-
Tianjihuang compound alleviates aflatoxin B1-induced hepatic steatosis and fibrosis by targeting PPARα-TGF-β pathway in ducklings.Poult Sci. 2025 Apr;104(4):105006. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105006. Epub 2025 Mar 8. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40073684 Free PMC article.
-
CellFM: a large-scale foundation model pre-trained on transcriptomics of 100 million human cells.Nat Commun. 2025 May 20;16(1):4679. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59926-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40393991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gizachew D., Chang C.H., Szonyi B., De La Torre S., Ting W.E. Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) Production by Aspergillus Flavus and Aspergillus Parasiticus on Ground Nyjer Seeds: The Effect of Water Activity and Temperature. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019;296:8–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.02.017. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

