TROLLOPE: A novel sequence-based stacked approach for the accelerated discovery of linear T-cell epitopes of hepatitis C virus
- PMID: 37624802
- PMCID: PMC10456195
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290538
TROLLOPE: A novel sequence-based stacked approach for the accelerated discovery of linear T-cell epitopes of hepatitis C virus
Abstract
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a concerning health issue that causes chronic liver diseases. Despite many successful therapeutic outcomes, no effective HCV vaccines are currently available. Focusing on T cell activity, the primary effector for HCV clearance, T cell epitopes of HCV (TCE-HCV) are considered promising elements to accelerate HCV vaccine efficacy. Thus, accurate and rapid identification of TCE-HCVs is recommended to obtain more efficient therapy for chronic HCV infection. In this study, a novel sequence-based stacked approach, termed TROLLOPE, is proposed to accurately identify TCE-HCVs from sequence information. Specifically, we employed 12 different sequence-based feature descriptors from heterogeneous perspectives, such as physicochemical properties, composition-transition-distribution information and composition information. These descriptors were used in cooperation with 12 popular machine learning (ML) algorithms to create 144 base-classifiers. To maximize the utility of these base-classifiers, we used a feature selection strategy to determine a collection of potential base-classifiers and integrated them to develop the meta-classifier. Comprehensive experiments based on both cross-validation and independent tests demonstrated the superior predictive performance of TROLLOPE compared with conventional ML classifiers, with cross-validation and independent test accuracies of 0.745 and 0.747, respectively. Finally, a user-friendly online web server of TROLLOPE (http://pmlabqsar.pythonanywhere.com/TROLLOPE) has been developed to serve research efforts in the large-scale identification of potential TCE-HCVs for follow-up experimental verification.
Copyright: © 2023 Charoenkwan et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

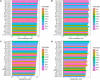
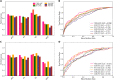
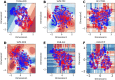
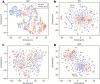
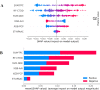
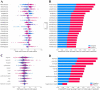
References
-
- Dustin L. B., Bartolini B., Capobianchi M. R., and Pistello M., "Hepatitis C virus: life cycle in cells, infection and host response, and analysis of molecular markers influencing the outcome of infection and response to therapy," Clin Microbiol Infect, vol. 22, no. 10, pp. 826–832, Oct 2016. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2016.08.025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

