Modular architecture facilitates noise-driven control of synchrony in neuronal networks
- PMID: 37624893
- PMCID: PMC10456864
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ade1755
Modular architecture facilitates noise-driven control of synchrony in neuronal networks
Abstract
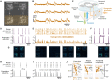
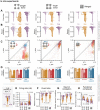
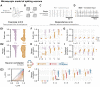
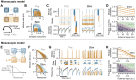
High-level information processing in the mammalian cortex requires both segregated processing in specialized circuits and integration across multiple circuits. One possible way to implement these seemingly opposing demands is by flexibly switching between states with different levels of synchrony. However, the mechanisms behind the control of complex synchronization patterns in neuronal networks remain elusive. Here, we use precision neuroengineering to manipulate and stimulate networks of cortical neurons in vitro, in combination with an in silico model of spiking neurons and a mesoscopic model of stochastically coupled modules to show that (i) a modular architecture enhances the sensitivity of the network to noise delivered as external asynchronous stimulation and that (ii) the persistent depletion of synaptic resources in stimulated neurons is the underlying mechanism for this effect. Together, our results demonstrate that the inherent dynamical state in structured networks of excitable units is determined by both its modular architecture and the properties of the external inputs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The number of synaptic inputs and the synchrony of large, sparse neuronal networks.Neural Comput. 2000 May;12(5):1095-139. doi: 10.1162/089976600300015529. Neural Comput. 2000. PMID: 10905810
-
Synchronization properties of networks of electrically coupled neurons in the presence of noise and heterogeneities.J Comput Neurosci. 2009 Jun;26(3):369-92. doi: 10.1007/s10827-008-0117-3. Epub 2008 Nov 26. J Comput Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19034642
-
Reconfiguration of Brain Network Architectures between Resting-State and Complexity-Dependent Cognitive Reasoning.J Neurosci. 2017 Aug 30;37(35):8399-8411. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0485-17.2017. Epub 2017 Jul 31. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28760864 Free PMC article.
-
Portraits of communication in neuronal networks.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019 Feb;20(2):117-127. doi: 10.1038/s41583-018-0094-0. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30552403 Review.
-
Integration of Feedforward and Feedback Information Streams in the Modular Architecture of Mouse Visual Cortex.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2023 Jul 10;46:259-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-083122-021241. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36972612 Review.
Cited by
-
Open problems in synthetic multicellularity.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2024 Dec 31;10(1):151. doi: 10.1038/s41540-024-00477-8. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2024. PMID: 39741147 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities and Challenges of Brain-on-a-Chip Interfaces.Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2025 Jun 17;6:0287. doi: 10.34133/cbsystems.0287. eCollection 2025. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2025. PMID: 40530005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances and applications of human brain models.Front Neural Circuits. 2024 Aug 5;18:1453958. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2024.1453958. eCollection 2024. Front Neural Circuits. 2024. PMID: 39161368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modular architecture confers robustness to damage and facilitates recovery in spiking neural networks modeling in vitro neurons.Front Neurosci. 2025 Jun 19;19:1570783. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1570783. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40613085 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous Dynamics Predict the Effects of Targeted Intervention in Hippocampal Neuronal Cultures.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 1:2025.04.29.651327. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.29.651327. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40631130 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- A. Arieli, A. Sterkin, A. Grinvald, A. D. Aertsen, Dynamics of ongoing activity: Explanation of the large variability in evoked cortical responses. Science 273, 1868–1871 (1996). - PubMed
-
- J. Aru, J. Aru, V. Priesemann, M. Wibral, L. Lana, G. Pipa, W. Singer, R. Vicente, Untangling cross-frequency coupling in neuroscience. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 31, 51–61 (2015). - PubMed
-
- A. Fornito, A. Zalesky, E. Bullmore, in Fundamentals of brain network analysis. (Academic Press, 2016).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

