Airway stem cell reconstitution by the transplantation of primary or pluripotent stem cell-derived basal cells
- PMID: 37625411
- PMCID: PMC10528754
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.07.014
Airway stem cell reconstitution by the transplantation of primary or pluripotent stem cell-derived basal cells
Abstract
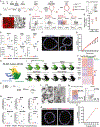
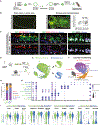
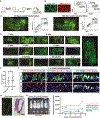
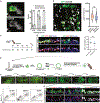
Life-long reconstitution of a tissue's resident stem cell compartment with engrafted cells has the potential to durably replenish organ function. Here, we demonstrate the engraftment of the airway epithelial stem cell compartment via intra-airway transplantation of mouse or human primary and pluripotent stem cell (PSC)-derived airway basal cells (BCs). Murine primary or PSC-derived BCs transplanted into polidocanol-injured syngeneic recipients give rise for at least two years to progeny that stably display the morphologic, molecular, and functional phenotypes of airway epithelia. The engrafted basal-like cells retain extensive self-renewal potential, evident by the capacity to reconstitute the tracheal epithelium through seven generations of secondary transplantation. Using the same approach, human primary or PSC-derived BCs transplanted into NOD scid gamma (NSG) recipient mice similarly display multilineage airway epithelial differentiation in vivo. Our results may provide a step toward potential future syngeneic cell-based therapy for patients with diseases resulting from airway epithelial cell damage or dysfunction.
Keywords: airway basal cells; airway epithelial stem cell transplantation; directed differentiation; pluripotent stem cells; regeneration.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors have filed a patent application related to the engraftment approach presented in this manuscript.
Figures



Comment in
-
Lung repair empowered by exogenous cells taking residence.Cell Stem Cell. 2023 Sep 7;30(9):1127-1129. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.08.008. Cell Stem Cell. 2023. PMID: 37683601
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R21 HD094012/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007035/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL134745/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139799/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030501/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095993/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL124392/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HL134763/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK065988/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL134766/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL148692/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020C00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

