Biochemical and genetic evidence supports Fyv6 as a second-step splicing factor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 37625852
- PMCID: PMC10578475
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.079607.123
Biochemical and genetic evidence supports Fyv6 as a second-step splicing factor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
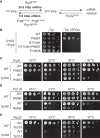
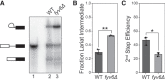
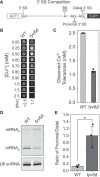
Precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) splicing is an essential process for gene expression in eukaryotes catalyzed by the spliceosome in two transesterification steps. The spliceosome is a large, highly dynamic complex composed of five small nuclear RNAs and dozens of proteins, some of which are needed throughout the splicing reaction while others only act during specific stages. The human protein FAM192A was recently proposed to be a splicing factor that functions during the second transesterification step, exon ligation, based on analysis of cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) density. It was also proposed that Fyv6 might be the Saccharomyces cerevisiae functional and structural homolog of FAM192A; however, no biochemical or genetic data has been reported to support this hypothesis. Herein, we show that Fyv6 is a splicing factor and acts during exon ligation. Deletion of FYV6 results in genetic interactions with the essential splicing factors Prp8, Prp16, and Prp22 and decreases splicing in vivo of reporter genes harboring intron substitutions that limit the rate of exon ligation. When splicing is assayed in vitro, whole-cell extracts lacking Fyv6 accumulate first-step products and exhibit a defect in exon ligation. Moreover, loss of Fyv6 causes a change in 3' splice site (SS) selection in both a reporter gene and the endogenous SUS1 transcript in vivo. Together, these data suggest that Fyv6 is a component of the yeast spliceosome that influences 3' SS usage and the potential homolog of human FAM192A.
Keywords: FAM192A; Fyv6; RNA splicing; spliceosome; yeast.
© 2023 Lipinski et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures





Update of
-
Biochemical and Genetic Evidence Supports Fyv6 as a Second-Step Splicing Factor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 31:2023.01.30.526368. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.30.526368. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: RNA. 2023 Nov;29(11):1792-1802. doi: 10.1261/rna.079607.123. PMID: 36778415 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M. 2009. Gephi: an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. Proc Int AAAI Conf Web Soc Media 3: 361–362. 10.1609/icwsm.v3i1.13937 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
