Novel VEGFR2 inhibitors with thiazoloquinoxaline scaffold targeting hepatocellular carcinoma with lower cardiotoxic impact
- PMID: 37626064
- PMCID: PMC10457369
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-40832-z
Novel VEGFR2 inhibitors with thiazoloquinoxaline scaffold targeting hepatocellular carcinoma with lower cardiotoxic impact
Abstract
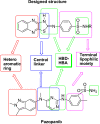
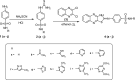
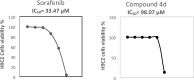
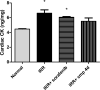
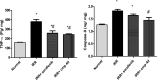
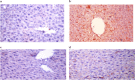
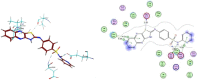
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a fatal tumor which is usually diagnosed at advanced stage. Molecular targeted drugs were used recently to treat HCC, however, due to serious side effects, mainly cardiotoxicity and emergence of resistance, there is demanding to explore new chemotherapeutics. 10 novel thiazoloquinoxaline derivatives coupled with different sulfonamide moieties 4(a-j) were designed and synthesized fulfilling pharmacophoric features of VEGFR-2 inhibition. Structures of all new compounds were verified via spectral and microanalytical data. After carrying in-vitro VEGFR-2 assay for compounds 4(a-j); sulfapyridine and sulfamethoxazole derivatives 4d and 4f showed potential inhibitory effect [61.04 and 83.35 nM], respectively, comparable to standard sorafenib [51.41 nM]. Both were then further evaluated for their cytocidal activity against HepG2 cell-line and against myocardium cells using H9C2 cell-line. As a result, only sulfapyridine derivative 4d exhibited a significant inhibition of HepG2 cells viability [IC50 = 4.31 μM]. Furthermore, it showed relatively lower cytotoxic impact against normal H9C2 myocardium cells [IC50, 33.47 μM] compared to that of sorafenib [IC50, 98.07 μM]. In-vivo study was carried out to determine myocardium safety of compound 4d on irradiated mice (8 Gy). In-vivo results of sulfapyridine derivative 4d showed normal cardiac enzyme function (CK) and serum catalase activity with significant reductions in LDH, cardiac TNF-α and caspase-9 levels, alongside with its efficacy in suppressing the expression of hepatic VEGF. In conclusion, sulfapyridine derivative 4d could be considered a promising candidate as VEGFR-2 inhibitor with less myocardium side effect.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
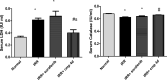
Similar articles
-
meta-Ureidophenoxy-1,2,3-triazole hybrid as a novel scaffold for promising HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma inhibitors: Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking studies.Bioorg Med Chem. 2022 Nov 15;74:117048. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2022.117048. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Bioorg Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36270111
-
Design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and modeling studies of novel conformationally-restricted analogues of sorafenib as selective kinase-inhibitory antiproliferative agents against hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Jan 15;210:113081. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.113081. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33310290
-
Treatment with a New Barbituric Acid Derivative Exerts Antiproliferative and Antimigratory Effects against Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Molecules. 2020 Jun 20;25(12):2856. doi: 10.3390/molecules25122856. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32575795 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the interplay between MMP-2, CA II and VEGFR-2 via new sulfonamide-tethered isomeric triazole hybrids; Microwave-assisted synthesis, computational studies and evaluation.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Jul;124:105816. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105816. Epub 2022 Apr 16. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 35489270 Review.
-
Novel benzothiazole-based dual VEGFR-2/EGFR inhibitors targeting breast and liver cancers: Synthesis, cytotoxic activity, QSAR and molecular docking studies.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022 Feb 15;58:128529. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128529. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35007724 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of thiazoloquinolinone derivatives: molecular docking, MD simulation, and pharmacological evaluation as VEGFR-2 inhibitors.BMC Chem. 2025 Apr 5;19(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13065-025-01459-5. BMC Chem. 2025. PMID: 40188066 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfonamides a Promising Hit for Cancer Therapy Through VEGFR-2 Inhibition.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 21;13(4):772. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13040772. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40299334 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sowa Y, Sakai T. Development of novel epigenetic molecular-targeting agents. Nihon Rinsho. 2015;73:1263–1267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

