Exploring the Pathogenesis and Mechanism-Targeted Treatments of Rosacea: Previous Understanding and Updates
- PMID: 37626650
- PMCID: PMC10452301
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11082153
Exploring the Pathogenesis and Mechanism-Targeted Treatments of Rosacea: Previous Understanding and Updates
Abstract
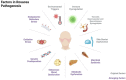
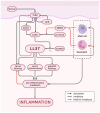
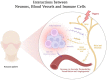
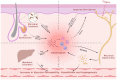
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by recurrent erythema, flushing, telangiectasia, papules, pustules, and phymatous changes in the central area of the face. Patients with this condition often experience a significant negative impact on their quality of life, self-esteem, and overall well-being. Despite its prevalence, the pathogenesis of rosacea is not yet fully understood. Recent research advances are reshaping our understanding of the underlying mechanisms of rosacea, and treatment options based on the pathophysiological perspective hold promise to improve patient outcomes and reduce incidence. In this comprehensive review, we investigate the pathogenesis of rosacea in depth, with a focus on emerging and novel mechanisms, and provide an up-to-date overview of therapeutic strategies that target the diverse pathogenic mechanisms of rosacea. Lastly, we discuss potential future research directions aimed at enhancing our understanding of the condition and developing effective treatments.
Keywords: inflammation; inflammatory skin disease; pathogenesis; rosacea; therapeutic strategies; treatment options.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rosacea Treatment: Review and Update.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021 Feb;11(1):13-24. doi: 10.1007/s13555-020-00461-0. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021. PMID: 33170491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rosacea: New Concepts in Classification and Treatment.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021 Jul;22(4):457-465. doi: 10.1007/s40257-021-00595-7. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33759078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacologic treatments for rosacea.Clin Dermatol. 2017 Mar-Apr;35(2):207-212. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2016.10.016. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Clin Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28274361
-
Rosacea Topical Treatment and Care: From Traditional to New Drug Delivery Systems.Mol Pharm. 2023 Aug 7;20(8):3804-3828. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c00324. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Mol Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37478169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acne and Rosacea.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2017 Jan;7(Suppl 1):43-52. doi: 10.1007/s13555-016-0168-8. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2017. PMID: 28150107 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing Ultrasonic Technologies to Treat Staphylococcus Aureus Skin Infections.Molecules. 2025 Jan 23;30(3):512. doi: 10.3390/molecules30030512. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39942617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of clinical characteristics of neurogenic rosacea and erythematotelangiectatic rosacea: a cross-sectional observational study.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2512123. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2512123. Epub 2025 May 28. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40434799 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Genomic and GEO Data Analysis Reveals Therapeutic Targets for Rosacea.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Jul;24(7):e70334. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70334. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40635520 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Zonulin and Its Role in Rosacea Pathogenesis: A Comprehensive Estimation Study.Dermatol Pract Concept. 2025 Jul 31;15(3):5027. doi: 10.5826/dpc.1503a5027. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2025. PMID: 40790428 Free PMC article.
-
30% Supramolecular Salicylic Acid Improved Symptoms and Skin Barrier in Papulopustular Rosacea.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Feb;24(2):e70046. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70046. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39968706 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Thiboutot D., Anderson R., Cook-Bolden F., Draelos Z., Gallo R.L., Granstein R.D., Kang S., Macsai M., Gold L.S., Tan J. Standard management options for rosacea: The 2019 update by the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020;82:1501–1510. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.01.077. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

