A Systematic Compilation of Human SH3 Domains: A Versatile Superfamily in Cellular Signaling
- PMID: 37626864
- PMCID: PMC10453029
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12162054
A Systematic Compilation of Human SH3 Domains: A Versatile Superfamily in Cellular Signaling
Abstract
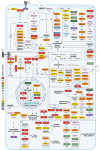
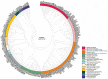
SRC homology 3 (SH3) domains are fundamental modules that enable the assembly of protein complexes through physical interactions with a pool of proline-rich/noncanonical motifs from partner proteins. They are widely studied modular building blocks across all five kingdoms of life and viruses, mediating various biological processes. The SH3 domains are also implicated in the development of human diseases, such as cancer, leukemia, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's disease, and various infections. A database search of the human proteome reveals the existence of 298 SH3 domains in 221 SH3 domain-containing proteins (SH3DCPs), ranging from 13 to 720 kilodaltons. A phylogenetic analysis of human SH3DCPs based on their multi-domain architecture seems to be the most practical way to classify them functionally, with regard to various physiological pathways. This review further summarizes the achievements made in the classification of SH3 domain functions, their binding specificity, and their significance for various diseases when exploiting SH3 protein modular interactions as drug targets.
Keywords: SH3 domain; SH3 domain-containing proteins; SRC homology 3; proline-rich motifs (PRM); protein interaction; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional Classification and Interaction Selectivity Landscape of the Human SH3 Domain Superfamily.Cells. 2024 Jan 20;13(2):195. doi: 10.3390/cells13020195. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38275820 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal Structure of the SH3 Domain of ASAP1 in Complex with the Proline Rich Motif (PRM) of MICAL1 Reveals a Unique SH3/PRM Interaction Mode.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 11;24(2):1414. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021414. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674928 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of Src homology 3 domain association with the proline-rich domain of dynamins: specificity, occlusion, and the effects of phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 17;280(24):23147-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501745200. Epub 2005 Apr 17. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15834155
-
The SH3 domain--a family of versatile peptide- and protein-recognition module.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:4938-52. doi: 10.2741/3053. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508559 Review.
-
Novel Roles of SH2 and SH3 Domains in Lipid Binding.Cells. 2021 May 13;10(5):1191. doi: 10.3390/cells10051191. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34068055 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Classification and Interaction Selectivity Landscape of the Human SH3 Domain Superfamily.Cells. 2024 Jan 20;13(2):195. doi: 10.3390/cells13020195. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38275820 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of variant interactions in families with autism points to genes involved in the development of the central nervous system.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 11;20(6):e0326022. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326022. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40498723 Free PMC article.
-
The Ubiquitin-Associated and SH3 Domain-Containing Proteins (UBASH3) Family in Mammalian Development and Immune Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 5;25(3):1932. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031932. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The conformation of the nSrc specificity-determining loop in the Src SH3 domain is modulated by a WX conserved sequence motif found in SH3 domains.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Dec 3;11:1487276. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1487276. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39698111 Free PMC article.
-
VHI-Pred: A Multi-Feature-Based Tool for Predicting Human-Virus Protein-Protein Interactions.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 5. doi: 10.1007/s12033-025-01417-5. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40186829
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

