The Adiponectin Receptor Agonist, ALY688: A Promising Therapeutic for Fibrosis in the Dystrophic Muscle
- PMID: 37626911
- PMCID: PMC10453606
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12162101
The Adiponectin Receptor Agonist, ALY688: A Promising Therapeutic for Fibrosis in the Dystrophic Muscle
Abstract
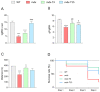
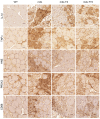
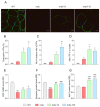
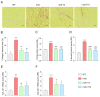
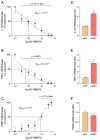
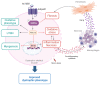
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is one of the most devastating myopathies, where severe inflammation exacerbates disease progression. Previously, we demonstrated that adiponectin (ApN), a hormone with powerful pleiotropic effects, can efficiently improve the dystrophic phenotype. However, its practical therapeutic application is limited. In this study, we investigated ALY688, a small peptide ApN receptor agonist, as a potential novel treatment for DMD. Four-week-old mdx mice were subcutaneously treated for two months with ALY688 and then compared to untreated mdx and wild-type mice. In vivo and ex vivo tests were performed to assess muscle function and pathophysiology. Additionally, in vitro tests were conducted on human DMD myotubes. Our results showed that ALY688 significantly improved the physical performance of mice and exerted potent anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative and anti-fibrotic actions on the dystrophic muscle. Additionally, ALY688 hampered myonecrosis, partly mediated by necroptosis, and enhanced the myogenic program. Some of these effects were also recapitulated in human DMD myotubes. ALY688's protective and beneficial properties were mainly mediated by the AMPK-PGC-1α axis, which led to suppression of NF-κβ and TGF-β. Our results demonstrate that an ApN mimic may be a promising and effective therapeutic prospect for a better management of DMD.
Keywords: ALY688; AMPK; adiponectin; duchenne muscular dystrophy; fibrosis; inflammation; myonecrosis; necroptosis; regeneration; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Recent Advances in Pre-Clinical Development of Adiponectin Receptor Agonist Therapies for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 25;12(7):1407. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071407. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39061981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The slow-release adiponectin analog ALY688-SR modifies early-stage disease development in the D2.mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Apr 1;326(4):C1011-C1026. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00638.2023. Epub 2023 Dec 25. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38145301
-
AdipoRon, a new therapeutic prospect for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020 Apr;11(2):518-533. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12531. Epub 2020 Jan 21. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020. PMID: 31965757 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle secretome in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a pivotal anti-inflammatory role of adiponectin.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Jul;74(13):2487-2501. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2465-5. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28188344 Free PMC article.
-
Memory impairment in the D2.mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy is prevented by the adiponectin receptor agonist ALY688.Exp Physiol. 2023 Sep;108(9):1108-1117. doi: 10.1113/EP091274. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Exp Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37415288 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Unravelling the Adiponectin Hallmark and Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Its Receptor Agonists in Cancer Metabolic Reprogramming.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 5;15(6):820. doi: 10.3390/biom15060820. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances and challenges of targeting epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) and perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT).Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Aug 4;24(1):319. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02763-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40760703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Pre-Clinical Development of Adiponectin Receptor Agonist Therapies for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 25;12(7):1407. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071407. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39061981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a non-invasive bioassay for adiponectin target engagement in mice.iScience. 2024 Sep 19;27(10):110994. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110994. eCollection 2024 Oct 18. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39435143 Free PMC article.
-
Striking Cardioprotective Effects of an Adiponectin Receptor Agonist in an Aged Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Dec 18;13(12):1551. doi: 10.3390/antiox13121551. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharyya S., Villalta S.A., Bakkar N., Bupha-Intr T., Janssen P.M., Carathers M., Li Z.W., Beg A.A., Ghosh S., Sahenk Z., et al. Interplay of IKK/NF-kappaB signaling in macrophages and myofibers promotes muscle degeneration in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J. Clin. Investig. 2007;117:889–901. doi: 10.1172/JCI30556. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

