3D Culture and Interferon-γ Priming Modulates Characteristics of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells by Modifying the Expression of Both Intracellular and Exosomal microRNAs
- PMID: 37626949
- PMCID: PMC10451847
- DOI: 10.3390/biology12081063
3D Culture and Interferon-γ Priming Modulates Characteristics of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells by Modifying the Expression of Both Intracellular and Exosomal microRNAs
Abstract
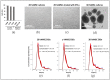
Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (MSCs) have emerged as a therapeutic tool in regenerative medicine. Recent studies have shown that exosome (EXO)-derived microRNAs (miRNAs) play a crucial role in mediating MSC functions. Additionally, intracellular miRNAs have been found to regulate MSC therapeutic capacities. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying miRNA-mediated MSC effects are not fully understood. We used 3D culture and IFN-γ to prime/enhance the MSC therapeutic effects in terms of functional miRNAs. After priming, our analysis revealed stable variations in intracellular miRNA among the MSC biological replicates. Conversely, a significant variability of miRNA was observed among EXOs released from biological replicates of the priming treatment. For each priming, we observed distinct miRNA expression profiles between the MSCs and their EXOs. Moreover, in both types of priming, gene ontology (GO) analysis of deregulated miRNAs highlighted their involvement in tissue repair/regeneration pathways. In particular, the 3D culture enhanced angiogenic properties in both MSCs and EXOs, while IFN-γ treatment enriched miRNAs associated with immunomodulatory pathways. These findings suggest that 3D culture and IFN-γ treatment are promising strategies for enhancing the therapeutic potential of MSCs by modulating miRNA expression. Additionally, the identified miRNAs may contribute to understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the miRNA-mediated therapeutic effects of MSCs.
Keywords: IFN-γ priming; MSC priming; MSC spheroids; MSC therapeutic properties; exosomes; mesenchymal stromal/stem cells; microRNAs; regenerative medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Margiana R., Markov A., Zekiy A.O., Hamza M.U., Al-Dabbagh K.A., Al-Zubaidi S.H., Hameed N.M., Ahmad I., Sivaraman R., Kzar H.H., et al. Clinical application of mesenchymal stem cell in regenerative medicine: A narrative review. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022;13:366. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03054-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Miceli V., Zito G., Bulati M., Gallo A., Busa R., Iannolo G., Conaldi P.G. Different priming strategies improve distinct therapeutic capabilities of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells: Potential implications for their clinical use. World J. Stem Cells. 2023;15:400–420. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i5.400. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

