Following the Pathway of W Chromosome Differentiation in Triportheus (Teleostei: Characiformes)
- PMID: 37626998
- PMCID: PMC10452202
- DOI: 10.3390/biology12081114
Following the Pathway of W Chromosome Differentiation in Triportheus (Teleostei: Characiformes)
Abstract
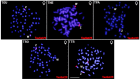
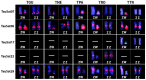
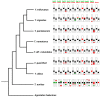
In this work, we trace the dynamics of satellite DNAs (SatDNAs) accumulation and elimination along the pathway of W chromosome differentiation using the well-known Triportheus fish model. Triportheus stands out due to a conserved ZZ/ZW sex chromosome system present in all examined species. While the Z chromosome is conserved in all species, the W chromosome is invariably smaller and exhibits differences in size and morphology. The presumed ancestral W chromosome is comparable to that of T. auritus, and contains 19 different SatDNA families. Here, by examining five additional Triportheus species, we showed that the majority of these repetitive sequences were eliminated as speciation was taking place. The W chromosomes continued degeneration, while the Z chromosomes of some species began to accumulate some TauSatDNAs. Additional species-specific SatDNAs that made up the heterochromatic region of both Z and W chromosomes were most likely amplified in each species. Therefore, the W chromosomes of the various Triportheus species have undergone significant evolutionary changes in a short period of time (15-25 Myr) after their divergence.
Keywords: FISH; cytogenomics; satellite DNA; sex chromosomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Ohno S. Sex Chromosomes and Sex-Linked Genes. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 1967. pp. 123–135.
-
- Bull J.J. Evolution of Sex Determining Mechanisms. Benjamin/Cummings; San Francisco, CA, USA: 1983.
-
- Rice W.R. Evolution of the Y sex chromosome in animals. Bioscience. 1996;46:331–343. doi: 10.2307/1312947. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

