Phenolic Extract from Olive Leaves as a Promising Endotherapeutic Treatment against Xylella fastidiosa in Naturally Infected Olea europaea (var. europaea) Trees
- PMID: 37627025
- PMCID: PMC10452569
- DOI: 10.3390/biology12081141
Phenolic Extract from Olive Leaves as a Promising Endotherapeutic Treatment against Xylella fastidiosa in Naturally Infected Olea europaea (var. europaea) Trees
Abstract
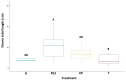
(1) Background: Since 2013, the pathogenic bacterium Xylella fastidiosa has been severely affecting olive production in Apulia, Italy, with consequences for the economy, local culture, landscape and biodiversity. The production of a phenolic extract from fresh olive leaves was employed for endotherapeutic injection into naturally infected olive trees by Xylella fastidiosa in Apulia region, Italy. (2) Methods: The effectiveness of the extract was tested in vitro and in planta in comparison with analogous treatments based on garlic powder and potassium phosphite. (3) Results: The uptake of phenolic compounds from olive leaves through a trunk injection system device resulted in a statistically significant increase in leaf area index and leaf area density, as well as in the growth of newly formed healthy shoots. Plant growth-promoting effects were also observed for potassium phosphite. Moreover, the bacteriostatic activities of the phenolic extract and of the garlic-powder-based solution have been demonstrated in in vitro tests. (4) Conclusions: The results obtained and the contained costs of extraction make the endotherapeutic treatment with phenolic compounds a promising strategy for controlling X fastidiosa to be tested on a larger scale, although the experiments conducted in this study proved not to be suitable for centenary trees.
Keywords: Olea europaea L.; Xylella fastidiosa; endotherapy; polar phenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Wells J.M., Raju B.C., Hung H.-Y., Weisburg W.G., Mandelco-Paul L., Brenner D.J. Xylella fastidiosa Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov: Gram-Negative, Xylem-Limited, Fastidious Plant Bacteria Related to Xanthomonas spp. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1987;37:136–143. doi: 10.1099/00207713-37-2-136. - DOI
-
- Saponari M., Boscia D., Nigro F., Martelli G.P. Identification of DNA Sequences Related to Xylella fastidiosa in Oleander, Almond and Olive Trees Exhibiting Leaf Scorch Symptoms in Apulia (Southern Italy) J. Plant Pathol. 2013;95:668.
-
- Cariddi C., Saponari M., Boscia D., De Stradis A., Loconsole G., Nigro F., Porcelli F., Potere O., Martelli G.P. Isolation of a Xylella fastidiosa Strain Infecting Olive and Oleander in Apulia, Italy. J. Plant Pathol. 2014;96:1–5. doi: 10.4454/JPP.V96I2.024. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

