IMP3 Expression as a Potential Tumour Marker in High-Risk Localisations of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: IMP3 in Metastatic cSCC
- PMID: 37627115
- PMCID: PMC10452512
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15164087
IMP3 Expression as a Potential Tumour Marker in High-Risk Localisations of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: IMP3 in Metastatic cSCC
Abstract
Background: High IMP3 expression is correlated with a worse outcome. Until now, there have been no data about IMP3 expression and clinical outcome for high-risk localisation of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin (cSCC).
Methods: One-hundred twenty-two patients with cSCC of the lip and ear were included, and IMP3 expression in the tumours was immunohistochemically assessed in different evaluation approaches. Subsequently, subgroups were analysed in a matched pair approach and correlated with clinical pathologic parameters. In the following, different IMP3 analysis methods were tested for clinical suitability.
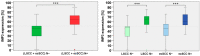
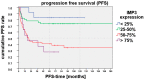
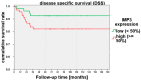
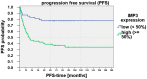
Results: We found a significant correlation between IMP3 expression and risk for lymph node metastasis, local relapse, and progression-free survival.
Conclusions: On basis of our data, we suggest a prognostic benefit cutoff value for high (>50%) and low (<50%) IMP3 expression. Thus, IMP3 expression has a high scientific potential for further studies and could potentially be used as a prognostic marker in diagnostic and therapeutic decision-making.
Keywords: HNSCC; IMP3; ear cancer; lip cancer; skin cancer; squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Leiter U., Heppt M.V., Steeb T., Amaral T., Bauer A., Becker J.C., Breitbart E., Breuninger H., Diepgen T., Dirschka T., et al. S3 Guideline for Actinic Keratosis and Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (CSCC)—Short Version, Part 2: Epidemiology, Surgical and Systemic Treatment of CSCC, Follow-up, Prevention and Occupational Disease. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. J. Ger. Soc. Dermatol. JDDG. 2020;18:400–413. doi: 10.1111/ddg.14072. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

