Where to Draw the LINE-Are Retrotransposable Elements Here to Stay?
- PMID: 37627147
- PMCID: PMC10452504
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15164119
Where to Draw the LINE-Are Retrotransposable Elements Here to Stay?
Abstract
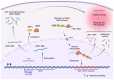
The frequency of somatic retrotranspositions of Long Interspersed Nuclear Elements 1 (LINE1) over a lifetime in healthy colonic epithelium and colorectal tumors has recently been reported. Indicative of a cell type-specific effect, LINE1 sequences in colonic epithelium showed lower levels of DNA methylation compared to other cell types examined in the study. Consistent with a role for DNA methylation in transposon silencing, the decreases in DNA methylation observed at LINE1 elements in colonic epithelium were accompanied by increases in LINE1 mRNA levels. In human primary colorectal tumors, LINE1 retrotransposition frequency was tenfold higher than in normal colonic tissues, with insertions potentially altering genomic stability and cellular functions. Here, we discuss the discoveries made by Nam and colleagues, emphasizing the intestinal-specific methylation signature regulating the LINE1 lifecycle and how this new information could shape future drug discovery endeavors against colorectal cancer.
Keywords: LINE1; colorectal cancer; epigenetics; methylation; retrotransposons; viral mimicry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vuik F.E., Nieuwenburg S.A., Bardou M., Lansdorp-Vogelaar I., Dinis-Ribeiro M., Bento M.J., Zadnik V., Pellisé M., Esteban L., Kaminski M.F., et al. Increasing incidence of colorectal cancer in young adults in Europe over the last 25 years. Gut. 2019;68:1820–1826. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317592. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Szigeti K.A., Kalmár A., Galamb O., Valcz G., Barták B.K., Nagy Z.B., Zsigrai S., Felletár I., Patai Á.V., Micsik T., et al. Global DNA hypomethylation of colorectal tumours detected in tissue and liquid biopsies may be related to decreased methyl-donor content. BMC Cancer. 2022;22:605. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09659-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

