The Role of GAB1 in Cancer
- PMID: 37627207
- PMCID: PMC10453317
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15164179
The Role of GAB1 in Cancer
Abstract
GRB2-associated binder 1 (GAB1) is the inaugural member of the GAB/DOS family of pleckstrin homology (PH) domain-containing proteins. Upon receiving various stimuli, GAB1 transitions from the cytoplasm to the membrane where it is phosphorylated by a range of kinases. This event recruits SH2 domain-containing proteins like SHP2, PI3K's p85 subunit, CRK, and others, thereby activating distinct signaling pathways, including MAPK, PI3K/AKT, and JNK. GAB1-deficient embryos succumb in utero, presenting with developmental abnormalities in the heart, placenta, liver, skin, limb, and diaphragm myocytes. Oncogenic mutations have been identified in the context of cancer. GAB1 expression levels are disrupted in various tumors, and elevated levels in patients often portend a worse prognosis in multiple cancer types. This review focuses on GAB1's influence on cellular transformation particularly in proliferation, evasion of apoptosis, metastasis, and angiogenesis-each of these processes being a cancer hallmark. GAB1 also modulates the resistance/sensitivity to antitumor therapies, making it a promising target for future anticancer strategies.
Keywords: GAB1; angiogenesis; metastasis; therapy resistance; tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

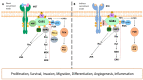

Similar articles
-
The multi-site docking protein Grb2-associated binder 1 (Gab1) enhances interleukin-6-induced MAPK-pathway activation in an SHP2-, Grb2-, and time-dependent manner.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Oct 24;17(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0451-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31651330 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Gab1 in heart, placenta, and skin development and growth factor- and cytokine-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase activation.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 May;20(10):3695-704. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.10.3695-3704.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10779359 Free PMC article.
-
The multisubstrate adapter Gab1 regulates hepatocyte growth factor (scatter factor)-c-Met signaling for cell survival and DNA repair.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;21(15):4968-84. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.15.4968-4984.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11438654 Free PMC article.
-
Essential roles of Gab1 tyrosine phosphorylation in growth factor-mediated signaling and angiogenesis.Int J Cardiol. 2015 Feb 15;181:180-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.10.148. Epub 2014 Oct 24. Int J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25528308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multiple function of Grb2 associated binder (Gab) adaptor/scaffolding protein in immune cell signaling.Immunol Lett. 2006 Apr 15;104(1-2):76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2005.11.017. Epub 2005 Dec 13. Immunol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16386802 Review.
Cited by
-
Toxicological landscape of Fuzi: a comprehensive study on the spatial distribution of toxicants and regional neurotoxicity variability in zebrafish.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 5;15:1500527. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1500527. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39975580 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective and vasoprotective effects of herb pair of Zhiqiao-Danggui in ischemic stroke uncovered by LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics approach.Metab Brain Dis. 2024 Aug;39(6):1131-1148. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01387-8. Epub 2024 Jul 13. Metab Brain Dis. 2024. PMID: 39002017
-
PI3K-dependent GAB1/Erk phosphorylation renders head and neck squamous cell carcinoma sensitive to PI3Kα inhibitors.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Jun 18;16(1):457. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07767-x. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40533463 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Targets for Epstein-Barr Virus BART MicroRNAs in B Cell Lymphomas.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 19;16(20):3537. doi: 10.3390/cancers16203537. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456631 Free PMC article.
-
Shared and specific competing endogenous RNAs network mining in four digestive system tumors.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024 Nov 5;23:4271-4287. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.11.005. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 39669749 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

