Integrative Evaluation of the Clinical Significance Underlying Protein Arginine Methyltransferases in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 37627211
- PMCID: PMC10453297
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15164183
Integrative Evaluation of the Clinical Significance Underlying Protein Arginine Methyltransferases in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
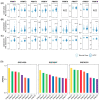
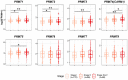
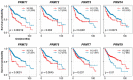
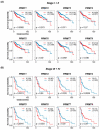
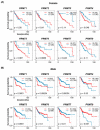
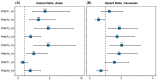
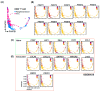
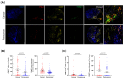
HCC is a major contributor to cancer-related mortality worldwide. Curative treatments are available for a minority of patients diagnosed at early stages; however, only a few multikinase inhibitors are available and are marginally effective in advanced cases, highlighting the need for novel therapeutic targets. One potential target is the protein arginine methyltransferase, which catalyzes various forms of arginine methylation and is often overexpressed in various cancers. However, the diverse expression patterns and clinical values of PRMTs in HCC remain unclear. In the present study, we evaluated the transcriptional expression of PRMTs in HCC cohorts using publicly available datasets. Our results revealed a significant association between PRMTs and prognosis in HCC patients with diverse clinical characteristics and backgrounds. This highlights the promising potential of PRMTs as prognostic biomarkers in patients with HCC. In particular, single-cell RNA (scRNA) sequencing analysis coupled with another human cohort study highlighted the pivotal role of PRMT1 in HCC progression, particularly in the context of Tex. Translating these findings into specific therapeutic decisions may address the unmet therapeutic needs of patients with HCC.
Keywords: T cell exhaustion; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognostic marker; protein arginine methyltransferase; protein methylation; tissue microarray.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protein arginine methyltransferases and hepatocellular carcinoma: A review.Transl Oncol. 2021 Nov;14(11):101194. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101194. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34365222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Classification molecular subtypes of hepatocellular carcinoma based on PRMT-related genes.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 22;14:1145408. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1145408. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36909154 Free PMC article.
-
Novel prognostic marker PRMT1 regulates cell growth via downregulation of CDKN1A in HCC.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 14;8(70):115444-115455. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23296. eCollection 2017 Dec 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29383172 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Study of Leishmania braziliensis Protein Arginine Methyltransferases (PRMTs) Reveals That PRMT1 and PRMT5 Are Required for Macrophage Infection.ACS Infect Dis. 2022 Mar 11;8(3):516-532. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00509. Epub 2022 Feb 28. ACS Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35226477
-
The protein arginine methyltransferase family (PRMTs) regulates metastases in various tumors: From experimental study to clinical application.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Nov;167:115456. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115456. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37696085 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of novel SND1 inhibitors by in silico-based molecular docking and dynamics simulation methods for managing hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 21;15(1):30701. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14878-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40841409 Free PMC article.
-
CDKN2 expression is a potential biomarker for T cell exhaustion in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMB Rep. 2024 Jun;57(6):287-292. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2023-0214. BMB Rep. 2024. PMID: 38523373 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin ligase Pellino1 targets STAT3 to regulate macrophage-mediated inflammation and tumor development.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 1;16(1):1256. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56440-6. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39893188 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Arginine Methyltransferases: Emerging Targets in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease.Diabetes Metab J. 2024 Jul;48(4):487-502. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0362. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Diabetes Metab J. 2024. PMID: 39043443 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

