Integrative Evaluation of the Clinical Significance Underlying Protein Arginine Methyltransferases in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 37627211
- PMCID: PMC10453297
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15164183
Integrative Evaluation of the Clinical Significance Underlying Protein Arginine Methyltransferases in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
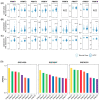
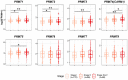
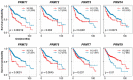
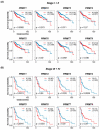
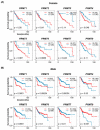
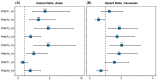
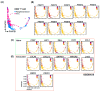
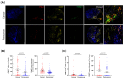
HCC is a major contributor to cancer-related mortality worldwide. Curative treatments are available for a minority of patients diagnosed at early stages; however, only a few multikinase inhibitors are available and are marginally effective in advanced cases, highlighting the need for novel therapeutic targets. One potential target is the protein arginine methyltransferase, which catalyzes various forms of arginine methylation and is often overexpressed in various cancers. However, the diverse expression patterns and clinical values of PRMTs in HCC remain unclear. In the present study, we evaluated the transcriptional expression of PRMTs in HCC cohorts using publicly available datasets. Our results revealed a significant association between PRMTs and prognosis in HCC patients with diverse clinical characteristics and backgrounds. This highlights the promising potential of PRMTs as prognostic biomarkers in patients with HCC. In particular, single-cell RNA (scRNA) sequencing analysis coupled with another human cohort study highlighted the pivotal role of PRMT1 in HCC progression, particularly in the context of Tex. Translating these findings into specific therapeutic decisions may address the unmet therapeutic needs of patients with HCC.
Keywords: T cell exhaustion; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognostic marker; protein arginine methyltransferase; protein methylation; tissue microarray.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

