Serum Soluble Lectin-like Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-1 (sLOX-1) Is Associated with Atherosclerosis Severity in Coronary Artery Disease
- PMID: 37627252
- PMCID: PMC10452248
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13081187
Serum Soluble Lectin-like Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-1 (sLOX-1) Is Associated with Atherosclerosis Severity in Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract
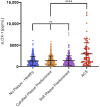
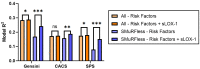
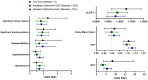
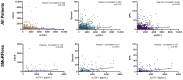
Risk-factor-based scoring systems for atherosclerotic coronary artery disease (CAD) remain concerningly inaccurate at the level of the individual and would benefit from the addition of biomarkers that correlate with atherosclerosis burden directly. We hypothesized that serum soluble lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (sLOX-1) would be independently associated with CAD and investigated this in the BioHEART study using 968 participants with CT coronary angiograms, which were scored for disease burden in the form of coronary artery calcium scores (CACS), Gensini scores, and a semi-quantitative soft-plaque score (SPS). Serum sLOX-1 was assessed by ELISA and was incorporated into regression models for disease severity and incidence. We demonstrate that sLOX-1 is associated with an improvement in the prediction of CAD severity when scored by Gensini or SPS, but not CACS. sLOX-1 also significantly improved the prediction of the incidence of obstructive CAD, defined as stenosis in any vessel >75%. The predictive value of sLOX-1 was significantly greater in the subgroup of patients who did not have any of the standard modifiable cardiovascular risk factors (SMuRFs). sLOX-1 is associated with CAD severity and is the first biomarker shown to have utility for risk prediction in the SMuRFless population.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; biomarker; computed tomography coronary angiography (CTCA); coronary artery disease (CAD); soluble lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (sLOX-1).
Conflict of interest statement
GAF reports personal consulting fees from CSL and grants from Abbott Diagnostic unrelated to the submitted work. In addition, GAF has a patent for Biomarkers and Oxidative Stress awarded, USA May 2017 (US9638699B2), issued to Northern Sydney Local Health District. The other authors have no disclosures. The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Gale C.P., Allan V., Cattle B.A., Hall A.S., West R.M., Timmis A., Gray H.H., Deanfield J., Fox K.A.A., Feltbower R. Trends in hospital treatments, including revascularisation, following acute myocardial infarction, 2003–2010: A multilevel and relative survival analysis for the National Institute for Cardiovascular Outcomes Research (NICOR) Heart. 2014;100:582–589. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2013-304517. - DOI - PubMed
-
- DeFilippis A.P., Young R., Carrubba C.J., McEvoy J.W., Budoff M.J., Blumenthal R.S., Kronmal R.A., McClelland R.L., Nasir K., Blaha M.J. An analysis of calibration and discrimination among multiple cardiovascular risk scores in a modern multiethnic cohort. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015;162:266–275. doi: 10.7326/M14-1281. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

