Senolytic Combination Treatment Is More Potent Than Single Drugs in Reducing Inflammatory and Senescence Burden in Cells from Painful Degenerating IVDs
- PMID: 37627322
- PMCID: PMC10452201
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13081257
Senolytic Combination Treatment Is More Potent Than Single Drugs in Reducing Inflammatory and Senescence Burden in Cells from Painful Degenerating IVDs
Abstract
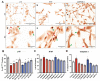
Background: Low back pain is a global health problem directly related to intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration. Senolytic drugs (RG-7112 and o-Vanillin) target and remove senescent cells from IVDs in vitro, improving tissue homeostasis. One drawback of using a single senolytic agent is the failure to target multiple senescent antiapoptotic pathways. This study aimed to determine if combining the two senolytic drugs, o-Vanillin and RG-7112, could more efficiently remove senescent cells and reduce the release of inflammatory factors and pain mediators in cells from degenerating human IVDs than either drug alone.
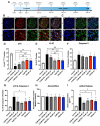
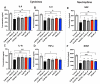
Methods: Preliminary data evaluating multiple concentrations of o-Vanillin and RG-7112 led to the selection of four treatment groups. Monolayer and pellet cultures of cells from painful degenerate IVDs were exposed to TLR-2/6 agonist. They were then treated with the senolytics o-Vanillin and RG7112 alone or combined. p16ink4a, Ki-67, caspase-3, inflammatory mediators, and neuronal sprouting were assessed.
Results: Compared to the single treatments, the combination of o-Vanillin and RG-7112 significantly reduced the amount of senescent IVD cells, proinflammatory cytokines, and neurotrophic factors. Moreover, both single and combination treatments significantly reduced neuronal sprouting in rat adrenal pheochromocytoma (PC-12 cells).
Conclusions: Combining o-Vanillin and RG-7112 greatly enhanced the effect of either senolytic alone. Together, these results support the potential of senolytics as a promising treatment for IVD-related low back pain.
Keywords: cellular senescence; combination therapy; intervertebral disc degeneration; low back pain; senolytics; senotherapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386:743–800. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

