The Potential Effects of Quercetin-Loaded Nanoliposomes on Amoxicillin/Clavulanate-Induced Hepatic Damage: Targeting the SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Microbiota Modulation
- PMID: 37627483
- PMCID: PMC10451903
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12081487
The Potential Effects of Quercetin-Loaded Nanoliposomes on Amoxicillin/Clavulanate-Induced Hepatic Damage: Targeting the SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Microbiota Modulation
Abstract
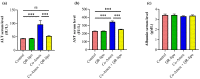
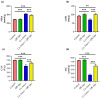
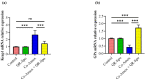
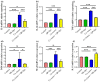
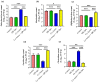
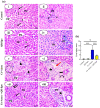
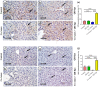
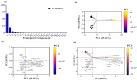
Amoxicillin/clavulanate (Co-Amox), a commonly used antibiotic for the treatment of bacterial infections, has been associated with drug-induced liver damage. Quercetin (QR), a naturally occurring flavonoid with pleiotropic biological activities, has poor water solubility and low bioavailability. The objective of this work was to produce a more bioavailable formulation of QR (liposomes) and to determine the effect of its intraperitoneal pretreatment on the amelioration of Co-Amox-induced liver damage in male rats. Four groups of rats were defined: control, QR liposomes (QR-lipo), Co-Amox, and Co-Amox and QR-lipo. Liver injury severity in rats was evaluated for all groups through measurement of serum liver enzymes, liver antioxidant status, proinflammatory mediators, and microbiota modulation. The results revealed that QR-lipo reduced the severity of Co-Amox-induced hepatic damage in rats, as indicated by a reduction in serum liver enzymes and total liver antioxidant capacity. In addition, QR-lipo upregulated antioxidant transcription factors SIRT1 and Nrf2 and downregulated liver proinflammatory signatures, including IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, NF-κB, and iNOS, with upregulation in the anti-inflammatory one, IL10. QR-lipo also prevented Co-Amox-induced gut dysbiosis by favoring the colonization of Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Bacteroides over Clostridium and Enterobacteriaceae. These results suggested that QR-lipo ameliorates Co-Amox-induced liver damage by targeting SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-κB and modulating the microbiota.
Keywords: Co-Amox-induced hepatotoxicity; SIRT1, Nrf2 and NF-κB targeting; gut dysbiosis; quercetin antioxidant activity; quercetin liposomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Limonin ameliorates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by activating Nrf2 antioxidative pathway and inhibiting NF-κB inflammatory response via upregulating Sirt1.Phytomedicine. 2020 Apr;69:153211. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153211. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32259676
-
The involvement of Nrf2 in the protective effects of diallyl disulfide on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic oxidative damage and inflammatory response in rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Jan;63:174-85. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.11.006. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24246655
-
Quercetin modulates NRF2 and NF-κB/TLR-4 pathways to protect against isoniazid- and rifampicin-induced hepatotoxicity in vivo.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021 Sep;99(9):952-963. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2021-0008. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33617360
-
[Role and mechanism of SIRT1 in regulating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in septic liver injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Jun;35(6):598-603. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220815-00744. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37366125 Chinese.
-
Gibberellic acid-induced hepatorenal dysfunction and oxidative stress: Mitigation by quercetin through modulation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic activities.J Food Biochem. 2022 Feb;46(2):e14069. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14069. Epub 2022 Jan 5. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 34984688
Cited by
-
Development of Fucoxanthin-Enriched Yogurt Using Nanoliposomal Carriers: A Strategy for Functional Dairy Products with Antioxidant and Erythroprotective Benefits.Molecules. 2025 Apr 21;30(8):1854. doi: 10.3390/molecules30081854. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40333899 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NF-κB signaling pathway in H2O2-induced oxidative stress of hiPSCs.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024 Oct;60(9):1021-1033. doi: 10.1007/s11626-024-00943-x. Epub 2024 Aug 12. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024. PMID: 39134871
-
The role of sirtuin1 in liver injury: molecular mechanisms and novel therapeutic target.PeerJ. 2024 Mar 29;12:e17094. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17094. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38563003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chrysin-loaded PEGylated liposomes protect against alloxan-induced diabetic neuropathy in rats: the interplay between endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy.Biol Res. 2024 Jul 9;57(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00521-1. Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 38982468 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative unified impact of magnetite iron nanoparticles and quercetin on broiler chickens: performance, antioxidant and immune defense and controlling of Clostridium perfringens infection.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Nov 7;11:1474942. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1474942. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39575436 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chalasani N., Bonkovsky H.L., Fontana R., Lee W., Stolz A., Talwalkar J., Reddy K.R., Watkins P.B., Navarro V., Barnhart H., et al. Features and outcomes of 899 patients with drug-induced liver injury: The DILIN prospective study. Gastroenterology. 2015;148:1340–1352. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.03.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jamshidi H.R., Negintaji S. Effects of Thymol on Co-amoxiclav-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats. Int. J. Med. Lab. 2021;8:44–54. doi: 10.18502/ijml.v8i1.5672. - DOI
-
- van Eyk A.D. Treatment of bacterial respiratory infections. S. Afr. Fam. Pract. 2019;61:8–15. doi: 10.4102/safp.v61i2.4984. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

