Modulation of TLR4/NFκB Pathways in Autoimmune Myocarditis
- PMID: 37627502
- PMCID: PMC10451772
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12081507
Modulation of TLR4/NFκB Pathways in Autoimmune Myocarditis
Abstract
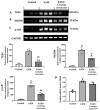
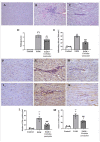
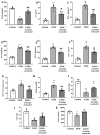
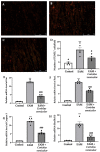
Myocarditis is an inflammatory and oxidative disorder characterized by immune cell recruitment in the damaged tissue and organ dysfunction. In this paper, we evaluated the molecular pathways involved in myocarditis using a natural compound, Coriolus versicolor, in an experimental model of autoimmune myocarditis (EAM). Animals were immunized with an emulsion of pig cardiac myosin and complete Freund's adjuvant supplemented with mycobacterium tuberculosis; thereafter, Coriolus versicolor (200 mg/Kg) was orally administered for 21 days. At the end of the experiment, blood pressure and heart rate measurements were recorded and the body and heart weights as well. From the molecular point of view, the Coriolus versicolor administration reduced the activation of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway and the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (INF-γ, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17, and IL-2) and restored the levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10). These anti-inflammatory effects were accompanied with a reduced lipid peroxidation and nitrite levels and restored the antioxidant enzyme activities (SOD and CAT) and GSH levels. Additionally, it reduced the histological injury and the immune cell recruitment (CD4+ and CD68+ cells). Moreover, we observed an antiapoptotic activity in both intrinsic (Fas/FasL/caspase-3) and extrinsic (Bax/Bcl-2) pathways. Overall, our data showed that Coriolus versicolor administration modulates the TLR4/NF-κB signaling in EAM.
Keywords: experimental autoimmune myocarditis; immunomodulation; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of Action of Natural Compounds in Peripheral Multiorgan Dysfunction and Hippocampal Neuroinflammation Induced by Sepsis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;12(3):635. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030635. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978883 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Sophora flavescens alkaloids and Panax quinquefolium saponins modulates different stages of experimental autoimmune myocarditis via the NF-κB and TGF-β1 pathways.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jul 14;24(3):570. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11507. eCollection 2022 Sep. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 36034755 Free PMC article.
-
Oleanolic acid modulates the immune-inflammatory response in mice with experimental autoimmune myocarditis and protects from cardiac injury. Therapeutic implications for the human disease.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Jul;72:250-62. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.04.002. Epub 2014 Apr 13. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24732212
-
[Time course of interleukin-21 and related cytokines expression in rats with experimental autoimmune myocarditis].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2012 Jan;40(1):43-9. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22490633 Chinese.
-
Natural products with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities against autoimmune myocarditis.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Oct;124:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.07.022. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28757189 Review.
Cited by
-
Biopolymers of Polycaprolactone Loaded with Caffeic Acid and Trametes versicolor Extract Induced Proliferation in Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells and Inhibited Platelet Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 21;26(10):4949. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104949. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40430091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elliott P., Andersson B., Arbustini E., Bilinska Z., Cecchi F., Charron P., Dubourg O., Kuhl U., Maisch B., McKenna W.J., et al. Classification of the cardiomyopathies: A position statement from the European Society Of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2008;29:270–276. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm342. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

