Antibiotic Resistance and Probiotics: Knowledge Gaps, Market Overview and Preliminary Screening
- PMID: 37627701
- PMCID: PMC10451169
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics12081281
Antibiotic Resistance and Probiotics: Knowledge Gaps, Market Overview and Preliminary Screening
Abstract
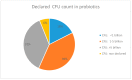
Probiotics are among those products, the use of which is increasing, and they are available primarily as food/dietary supplements, as well as in the form of medicines. This study aims to assess the attitudes and practices of health professionals and students of health sciences, give a short overview of the probiotics currently on the market, and conduct a screening of five food supplements and one drug with respect to antibiotic resistance. Nearly half of the respondents in our survey state that probiotics have no side effects, while only 6.3% believe that the use of probiotics can lead to antibiotic resistance. In addition, more than 40% of the participants throw unused probiotics into municipal waste. The market analysis results indicate that probiotic products on the Serbian market have highly variable CFU counts, while the declared health claims cover numerous beneficial health effects, and they are sometimes even registered as medicines. Lactobacilli are frequently present in probiotic supplements, and are sold in pharmacies and online. The experimental results showed that antibiotic resistance is present in different types of lactobacilli in probiotic products. The risk of using probiotics, regardless of their beneficial health effects, should be taken into account in the future. An update to the regulations governing probiotics, including a stipulation for antimicrobial resistance (AMR) testing, should be established, and guidelines for their proper use and disposal put into place.
Keywords: Lactobacillus; antibiotic resistance; antibiotic resistance screening; dietary supplements; market analysis; pharmacobiotic; probiotic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- International Probiotics Association, (IPA) Market Data, Probiotic Market 2021 and Trend Analysis. [(accessed on 15 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.ipaeurope.org/legal-framework/market-data/
-
- FAO/WHO. (Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization) Evaluation of Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Live Acid Bacteria. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation, Córdoba, Argentina. 2001. [(accessed on 30 May 2023)]. Available online: http://www.who.int/foodsafety/publications/fs_management/en/probiotics.p....
-
- Hill C., Guarner F., Reid G., Gibson G.R., Merenstein D.J., Pot B., Morelli L., Canani R.B., Flint H.J., Salminen S., et al. Expert consensus document: The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014;11:506–514. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

