Hybrid DAER Based Cross-Modal Retrieval Exploiting Deep Representation Learning
- PMID: 37628246
- PMCID: PMC10452985
- DOI: 10.3390/e25081216
Hybrid DAER Based Cross-Modal Retrieval Exploiting Deep Representation Learning
Abstract
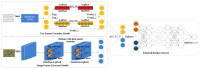
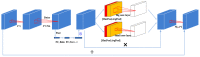
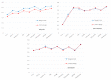
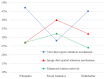
Information retrieval across multiple modes has attracted much attention from academics and practitioners. One key challenge of cross-modal retrieval is to eliminate the heterogeneous gap between different patterns. Most of the existing methods tend to jointly construct a common subspace. However, very little attention has been given to the study of the importance of different fine-grained regions of various modalities. This lack of consideration significantly influences the utilization of the extracted information of multiple modalities. Therefore, this study proposes a novel text-image cross-modal retrieval approach that constructs a dual attention network and an enhanced relation network (DAER). More specifically, the dual attention network tends to precisely extract fine-grained weight information from text and images, while the enhanced relation network is used to expand the differences between different categories of data in order to improve the computational accuracy of similarity. The comprehensive experimental results on three widely-used major datasets (i.e., Wikipedia, Pascal Sentence, and XMediaNet) show that our proposed approach is effective and superior to existing cross-modal retrieval methods.
Keywords: cross-modal retrieval; data augmentation; dual attention network; enhanced relation network.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modality-specific Cross-modal Similarity Measurement with Recurrent Attention Network.IEEE Trans Image Process. 2018 Jul 2. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2852503. Online ahead of print. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2018. PMID: 29994397
-
MHTN: Modal-Adversarial Hybrid Transfer Network for Cross-Modal Retrieval.IEEE Trans Cybern. 2020 Mar;50(3):1047-1059. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2879846. Epub 2018 Dec 5. IEEE Trans Cybern. 2020. PMID: 30530383
-
Deep Relation Embedding for Cross-Modal Retrieval.IEEE Trans Image Process. 2021;30:617-627. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3038354. Epub 2020 Dec 1. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2021. PMID: 33232230
-
Fine-Grained Cross-Modal Semantic Consistency in Natural Conservation Image Data from a Multi-Task Perspective.Sensors (Basel). 2024 May 14;24(10):3130. doi: 10.3390/s24103130. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38793984 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of deep cross-modal retrieval by generating real-valued representation.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2021 Apr 27;7:e491. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.491. eCollection 2021. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2021. PMID: 33987458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Z., Lu H., Fu H., Gu G. Image-text bidirectional learning network based cross-modal retrieval. Neurocomputing. 2022;483:148–159. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.02.007. - DOI
-
- Nagrani A., Albanie S., Zisserman A. Seeing voices and hearing faces: Cross-modal biometric matching; Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Salt Lake City, UT, USA. 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8427–8436.
-
- Yongjun Z., Yan E., Song I.Y. A natural language interface to a graph-based bibliographic information retrieval system. Data Knowl. Eng. 2017;111:73–89.
-
- Yuxin P., Jinwe Q., Yuxin Y. Modality-specific cross-modal similarity measurement with recurrent attention network. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018;27:5585–5599. - PubMed
-
- Gupta Y., Saini A., Saxena A. A new fuzzy logic based ranking function for efficient information retrieval system. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015;42:1223–1234. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2014.09.009. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

