Monitoring of the Healthy Neonatal Transition Period with Serial Lung Ultrasound
- PMID: 37628306
- PMCID: PMC10453359
- DOI: 10.3390/children10081307
Monitoring of the Healthy Neonatal Transition Period with Serial Lung Ultrasound
Abstract
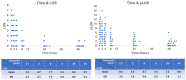
Ultrasound has been used to observe lung aeration and fluid clearance during the neonatal transition period, but there is no consensus regarding the optimal timing of lung ultrasound. We aimed to monitor the trend of the serial lung ultrasound score (LUS) and extended LUS (eLUS) throughout the neonatal transition period (≤1, 2, 4, 8, 24, and 48 h after birth), assess any correlation to the clinical presentation (using the Silverman Andersen Respiratory Severity Score (RSS)), and determine the optimal time of the ultrasound. We found both LUS and eLUS decreased significantly after 2 h of life and had similar statistical differences among the serial time points. Although both scores had a positive, moderate correlation to the RSS overall (Pearson correlation 0.499 [p < 0.001] between LUS and RSS, 0.504 [p < 0.001] between eLUS and RSS), the correlation was poor within 1 h of life (Pearson correlation 0.15 [p = 0.389] between LUS and RSS, 0.099 [p = 0.573] between eLUS and RSS). For better clinical correlation, the first lung ultrasound for the neonate may be performed at 2 h of life. Further research is warranted to explore the clinical value and limitations of earlier (≤1 h of life) lung ultrasound examinations.
Keywords: infant; lung liquid; lung ultrasound; neonatal transition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
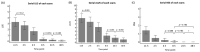
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

